OSU Pytheas UMS 3470 CNRS
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
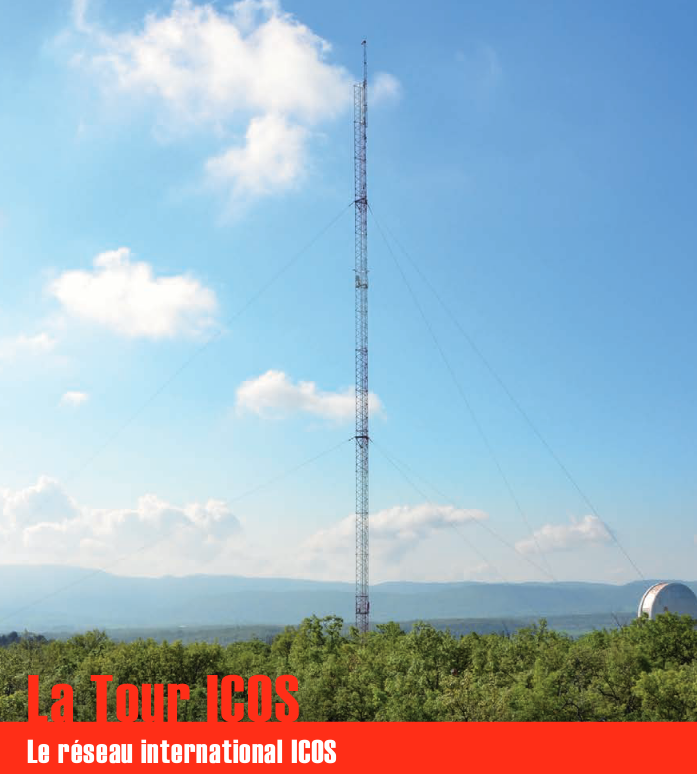

Une infrastructure de recherche européenne de mesure des concentrations atmosphériques des gaz à effet de serre et des flux de carbone sur les écosystèmes et l’océan. La tour ICOS (pour Integrated Carbon Observation System) installée à l'Observatoire de Haute Provence (OHP), haute de 100 m est une antenne régionale du dispositif permettant d’étudier la place de la forêt méditerranéenne dans le bilan de carbone. Elle est équipée d’instruments à trois niveaux (10, 50, 100 m). Le réseau est doté de 3 types de stations réparties sur le territoire : continentales, côtières et de montagne. Chacune de ces stations mesure les paramètres suivants : * température, direction et vitesse du vent, pression atmosphérique, humidité * CO2, CH4, CO, H2O * hauteur de couche limite atmosphérique (lidar) Les objectifs scientifiques de ce programme européen sont de : * tracer les flux de carbone en Europe et dans les régions adjacentes par observation des écosystèmes, de l'atmosphère et des océans à travers des réseaux intégrés, * fournir les observations à long terme nécessaires pour comprendre l'état présent et prévoir le comportement du carbone global et des émissions des gaz à effet de serre, * surveiller et évaluer l'efficacité de la séquestration du carbone et/ou de la réduction des émissions de gaz à effet de serre sur la composition globale de l'atmosphère, en prenant en compte les sources et les puits par région géographique et par secteur d'activité. L'infrastructure ICOS permet d'accueillir des chercheurs pour des campagnes de recherches
-
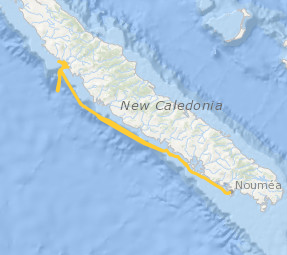
Le projet interdisciplinaire UECOCOT vise à développer des outils d'aide à la gestion durable des activités minières afin de permettre la meilleure cohabitation possible entre dynamique naturelle des environnements (et leur capacité de résistance aux dommages et de résilience) et les activités humaines (industrielles ou non). L'objectif global du projet est de répondre à la question " comment adapter , à un coût socio-économique acceptable, les activités minières pour que leur impact reste compatible avec la durabilité des écosystèmes côtiers et littoraux". Pour atteindre un tel objectif, le projet UECOCOT repose sur une approche multi-sites ayant des impacts miniers différents. Dans le Pacifique sud, le site choisi est le lagon de Koné (Nouvelle-Calédonie) à proximité duquel s'est implanté une mine de nickel et touché par des apports de particules riches en éléments métalliques (Ni, Cr, Co, Mn) issues de l'altération des massifs miniers latéritiques développés sur des péridotites. C'est dans ce cadre qu'a eu lieu en février 2018 une campagnes océanographique multidisciplinaire dans le lagon de Koné dont l'objectif était d'acquérir des informations sur : i) les flux hydrodynamiques et biogéochimiques entre la côte, le lagon et l'océan et les connectivités au sein même du lagon, ii) l'état écologique du lagon et son fonctionnement End to End (hydro-bio-géochimique) , iii) les apports miniers directs ou indirects (avec un focus sur les métaux) et leur impact sur le fonctionnement biogéochimique. L'ensemble des résultats acquis doit permettre de valider un modèle numérique de biologie intégrant les aspects physiologiques et comportementaux des organismes (plancton et benthos) liés à la contamination du milieu et à la circulation hydrodynamique au sein du lagon. Il doit en particulier aboutir à une meilleure compréhension du rôle de la barrière récifale sur la régulation hydrodynamique et ainsi permettre d'affiner les prévisions en terme de contamination du lagon suite à une modification de la structure récifale sous l'effet conjugué de contraintes anthropiques et climatiques. Ce projet s'inscrit dans le réseau international AMEDEE (Activité Minière, Environnement, Développement Economique, Ethiques) qui regroupe les programmes de R&D de 40 institutions scientifiques (Colin, 2016)
-
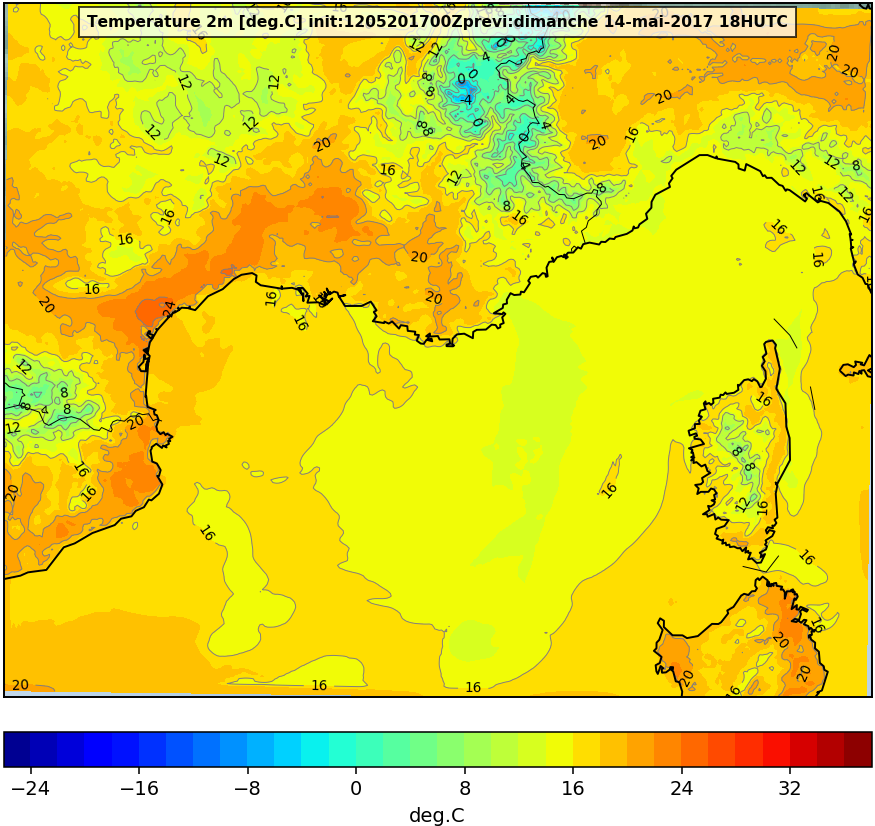
Sortie du modèle atmosphérique WRF et Meso-NH
-
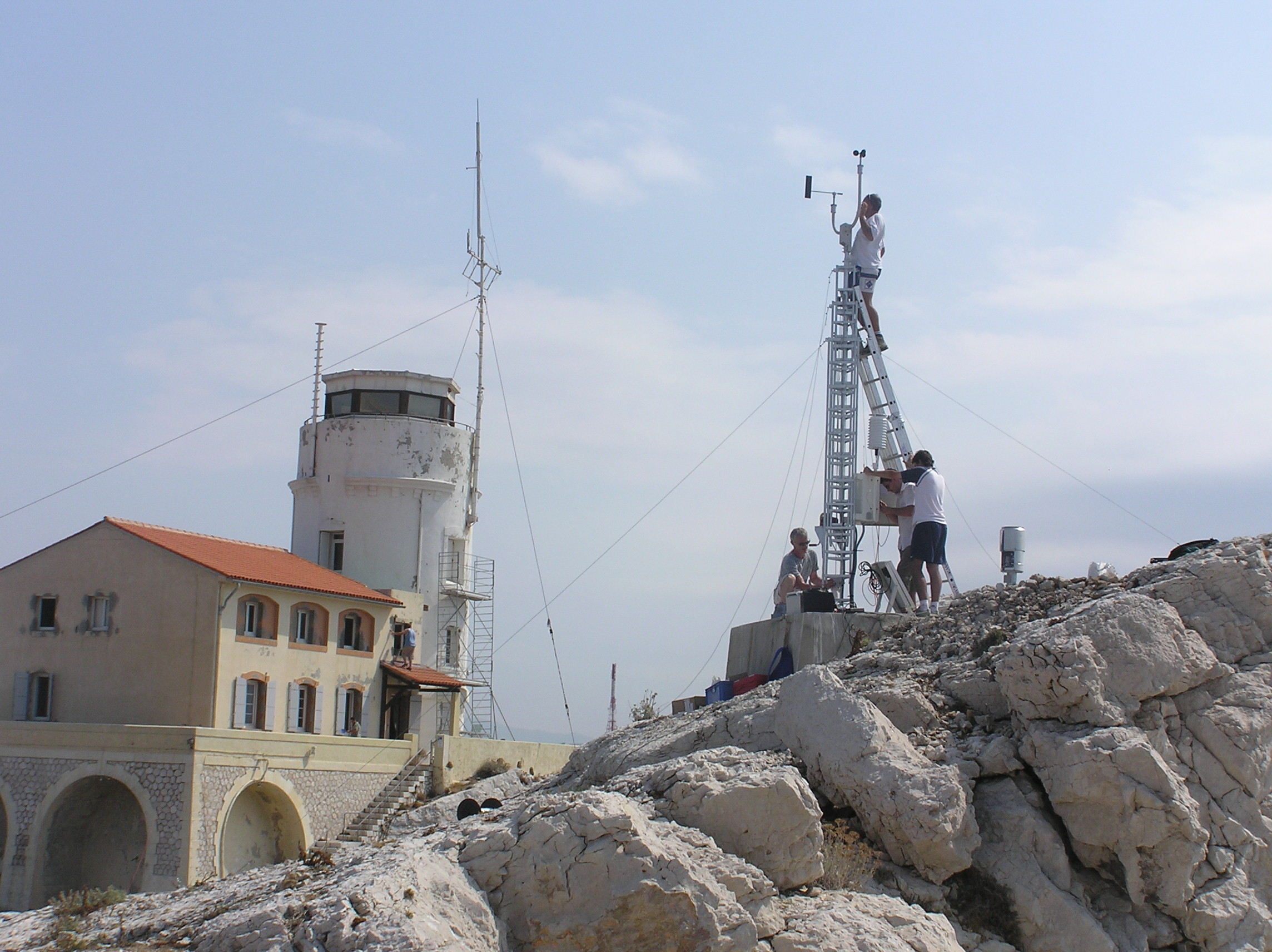

Meteorological data from the Bay of Marseille based on the measurements taken on the site located on the Pomegues island SITE : Iles de Pomègues – Sémaphore du Frioul - Latitude 43°15’59 N - Longitude 5°17’39 W - Hauteur : 25 m PROGRAMME DE RATTACHEMENT : - Mediterranean Oceanic Observing System on Environment : MOOSE - SOMLIT - Labellisation : SOERE - INSU - Financement : SOERE – INSU Read the abstract and supplemental information provided in the Vector template for more details. EQUIPEMENTS: - Station météorologique Auria avec transmission temps réel - Anémomètre et girouette - Baromètre - Pyranomètre - pluviomètre PARAMETRES MESURES : - Vent ( vitesse et direction) - Température et pression atmosphérique - Irradiance - Pluie DISPONIBLITE DES DONNEES : - Visualisation temps réel - Base de données du Service d'Observation du MIO RESPONSABLE : P. Raimbault (2019) D. Bourras (2024) PARTICIPANTS : - M. Fornier (Tech Univ) et M. Lafont (Tech Univ) : maintenance - Denis Bourras, Maurice Libes PARTENAIRES : - MOOSE - SOMLIT – MERMEX – CHARMEX -Ville de Marseille - Parc des îles du Frioul -CITATION : Raimbault, P., & Yohia, C. (2017). Météorologie locale en baie de Marseille : Frioul [Data set]. MIO UMR 7294 CNRS. https://doi.org/10.34930/5C9F6377-726B-436B-AA0F-ECC32803EF88
-
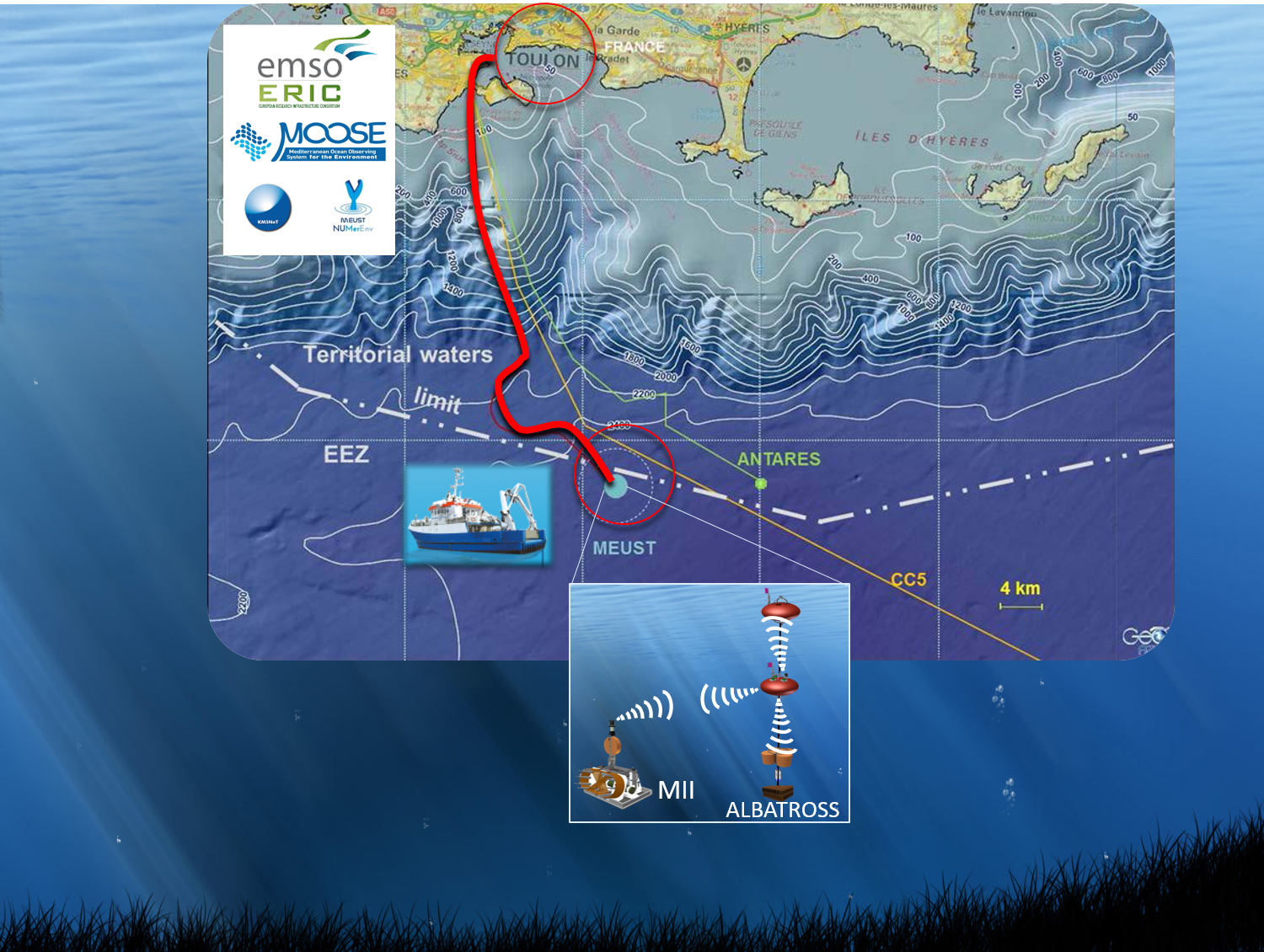
L'Observatoire européen multidisciplinaire des fonds marins et des colonnes d'eau baptisé (EMSO) (European Multidisciplinary Seafloor and water column Observatory) est une infrastructure de recherche répartie à l'échelle européenne des observatoires des fonds marins et des colonnes d'eau. Il vise à explorer davantage les océans, à mieux comprendre les phénomènes qui se produisent au fond de la mer, et à élucider le rôle critique que ces phénomènes jouent dans les systèmes terrestres globaux. Cet observatoire repose sur des sites (ou nœuds) d’observation qui ont été déployés dans des endroits stratégiques des mers européennes, de l'Arctique à l'Atlantique, de la Méditerranée à la mer Noire. Il y a actuellement onze nœuds en eau profonde plus quatre nœuds d'essai en eau peu profonde. EMSO Ligure Ouest est l’un de ces observatoires sous-marin permanent situé en mer Ligurienne et est déployé au large de Toulon, en France. Cette région été choisi pour ses intérêts scientifiques particulières tels que : sismicité, topographie, turbidité, biodiversité, dynamique des masses d'eau et flux de matières organiques. Ce réseau d’observation sous-marine fait aussi partie de KM3NeT (https://www.km3net.org/) qui a une topologie modulaire conçue pour connecter jusqu'à 120 unités de détection de neutrinos. L'instrumentation Earth and Sea Science (ESS) connectée à KM3NeT repose sur deux composants complémentaires: un module d'interface instrumenté (MII) et une ligne instrumentée autonome (ALBATROSS). La ligne ALBATROSS est une ligne inductive (2000 m) composée d'un système de communication acoustique, de deux câbles inductifs équipés de capteurs CTD-O2, de courantomètres et de deux bouées instrumentées. Cette ligne est déployée à une distance de 2-3 kilomètres du MII, et la communication à terre est faite par un lien acoustique avec le MII, et câble électro-optique via le nœud KM3NeT. Data 2016 - DOI: https://doi.org/10.17882/47129 Data Albatross inductive line from 2019 to 2020-11 - DOI: https://doi.org/10.17882/74513 Data Albatross inductive line from 2021 - DOI: https://doi.org/10.17882/83244
-
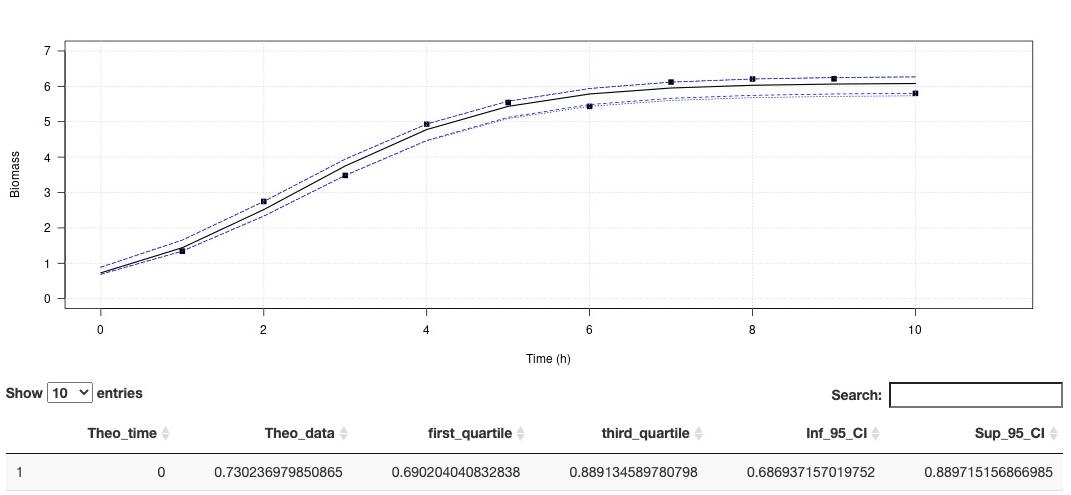
Environmental conditions are a set of physical and biological variables that define an ecosystem. Microorganisms with higher generation times than more complex multicellular organisms are more sensitive to changing environmental conditions. Therefore, microbial growth curves are an important and simple way to understand how environmental conditions affect microorganisms. Growth curves are used in a variety of biological applications. Traditionally in microbiology, the maximum growth rate (µmax) is calculated by fitting a linear model on data of the exponential growth phase. This method is simple to implement, and robust if the exponential phase contains many points. However, this method is very limiting when the curve is described with few points, as we have seen with experiments under high pressure conditions. In order to overcome this limit, recurrent in biology, we propose to use models to estimate growths parameters. Modeling has existed for many years to describe the growth behavior of microorganisms under variable physical and chemical conditions (Zwietering et al., 1990). Here we propose a ready-to-use application that do not require any special coding skills and allow retrieving several essential parameters describing microbial growth. his app aims at estimating the growth rate and maximum cells density using non-linear regression. The method is detailled in Martini et al. (2013). A demo dataset is available in "Download a demo dataset", you can save it in your computer and load it using "Browse", or you can also browse your own dataset. On Plot panel, it is possible to set axes labels, axes range and Smooth. Smooth parameter can compute theorical (downloadable) for to use with other activities. In order to run this application, you have to format your dataset with tabulation separators. Also, remove all spaces in the dataset header (prefer to use "_" when needed). Organise your dataset so that there is only two arrays. The first one being the time and the second one, the cells density (e. g. optic density, cell number, biomass). This application proposes a method to perform a logistic regression to estimate growth rate as well as maximum cells density . Citation: Garel, M., Izard, L., Vienne, M., Nerini, D., Tamburini, C., Martini, S. (2021). R-shiny-microorganisms v2 : A ready-to-use logistic regression implemented in R shiny to estimate growth parameters of microorganisms [Data set]. MIO UMR 7294 CNRS. https://doi.org/10.34930/DC1DAF1C-09E3-4829-8878-91D0BF0E643E
-
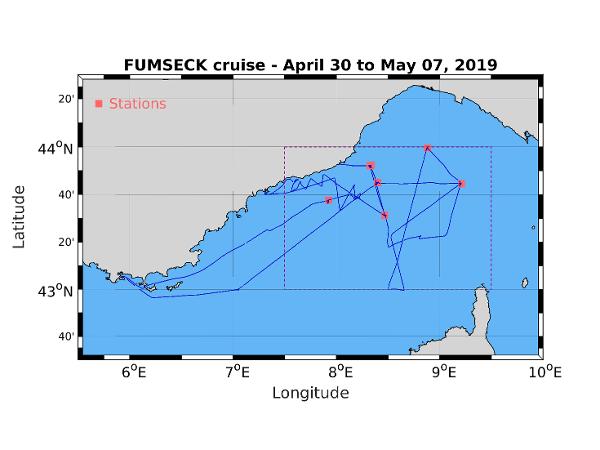
The FUMSECK (Facilities for Updating the Mediterranean Submesoscale - Ecosystem Coupling Knowledge) cruise aimed at performing technological tests of several instruments exploited for the study of the (sub)meso-scale processes and dynamics (from 0.1 to 100 km for a lifetime from several days to several weeks). Three categories of tests have been performed. The first category is the study of the MVP (Moving Vessel Profiler) tracked instruments behaviour, in particular the MSFFFII (Multi Sensor Free Fall Fish, so called "big fish"). We focused on the rotative behaviour of the big fish during its falling and raising, the connectics between the instrument and the MVP cable, between the platform and the boat depth sensor, and between the platform and the PC used to analyse the data, hence testing the whole data acquisition chain. The second category concerns the exploration of several methods to access the measurement of the current velocities vertical component, using different ADCP (Hull-mounted ADCP, Fixed-depth and profiling L-ADCP and Sentinel V (5 beams), Free-Fall ADCP), a prototype of a vertical velocity profiler, and a glider. Finally, we experimented the release of a sample of biodegradable coloured micro-particles at 15m-depth and within a 1 hectare surface, their tracking with drifting buoys, their extraction by pumping and their detection by cytometry. The goal of this experiment was its feasibility, in order to use these micro-particules as tracers for the understanding of the physical part of the ocean biological Carbon pump. Data acquired during the campain are : - Biological oceanography : * B08 Phytoplankton 7 days Continuous sampling for cytometer analysis. 15m-depth sampling for cytometer analysis (3 samples). 30.04.2019 * B90 Other biological/fisheries meas. 1 days GoPro images for the injection, the following and the sampling of coloured micro-particles. 30.04.2019 - Physical oceanography : * D05 Surface drifters/drifting buoys 3 deployments Injection, following, and sampling of coloured micro-particles at 15m-depth. Deployment and recovery of lagrangian drifters anchored at 15m for water mass following. 30.04.2019 * D71 Current profiler (eg ADCP) 7 days Continuous Vessel-Mounted ADCP. L-ADCP and Sentinel casts (5 and 6 stations). Free-Fall ADCP (6 stations). 30.04.2019 * D90 Other physical oceanographic meas. 7 days MVP (Moving Vessel Profiler) 30.04.2019 * D90 Other physical oceanographic meas. 6 stations VVP (Vertical Velocity Profiler) 30.04.2019 * H10 CTD stations 6 stations CTD casts 30.04.2019 * H71 Surface measurements underway (T,S) 7 days Continuous measurement 30.04.2019
-
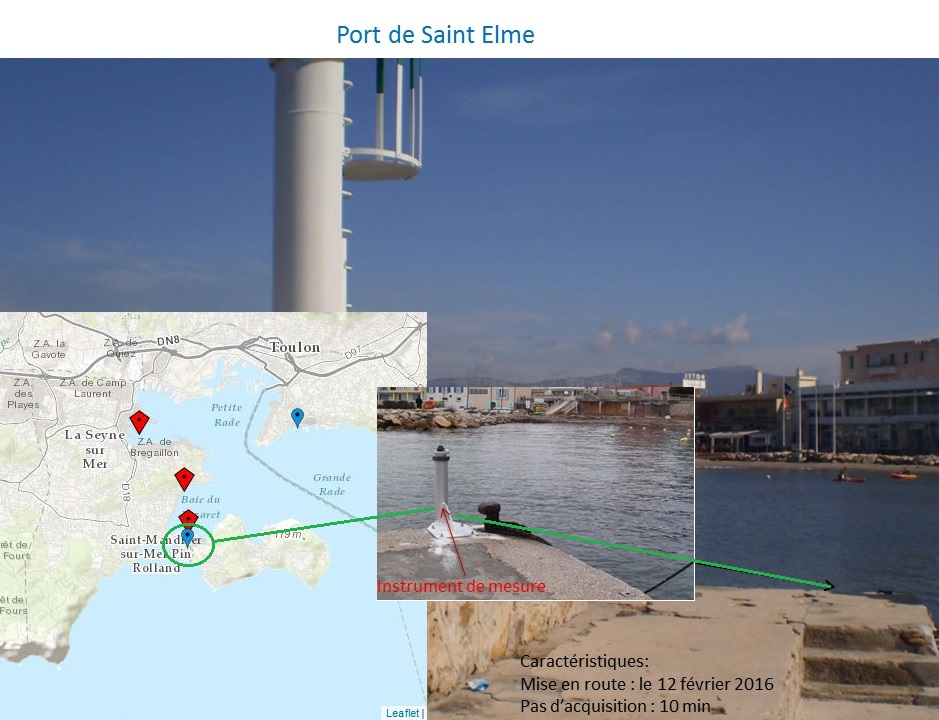
Acquisition automatique sur le long terme et en temps réel de données de niveau d'eau et de température le long du littoral Varois (France) Le programme consiste à apporter des données de mesures originales pour une meilleure compréhension et modélisation des interactions et couplages entre la dynamique côtière et la dynamique littorale à l'échelle des baies (actuellement aire de l'agglomération toulonnaise avec projet d'extension à plus grande échelle le long de la côte méditerranéenne), par le développement d'un système d'observation sur le long terme (plusieurs années). Il est à l'interface des axes de recherche en dynamique du plateau continental et en dynamique littorale du laboratoire MIO, composante de l'Observatoire des Sciences de l'Univers PYTHEAS.
-
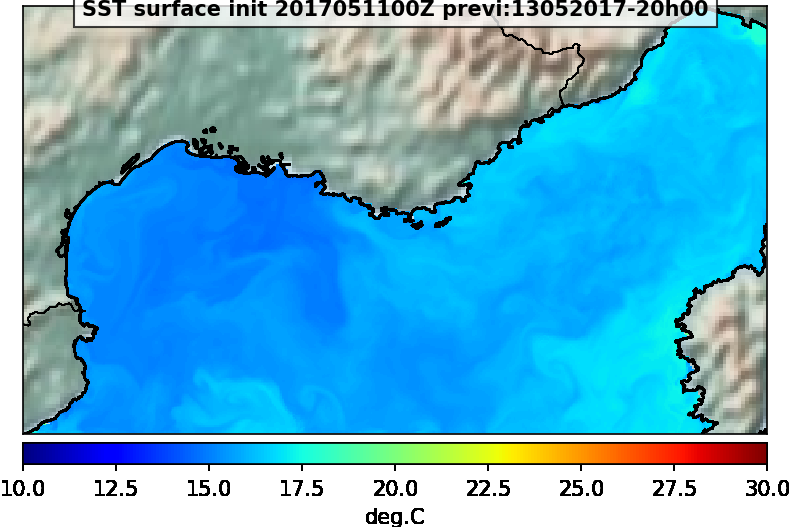
Sortie du modèle MARS3D-ECO3M. Les données disponibles sont la SST, la salinité, la vitesse et direction du courant et la chlorophylle
-
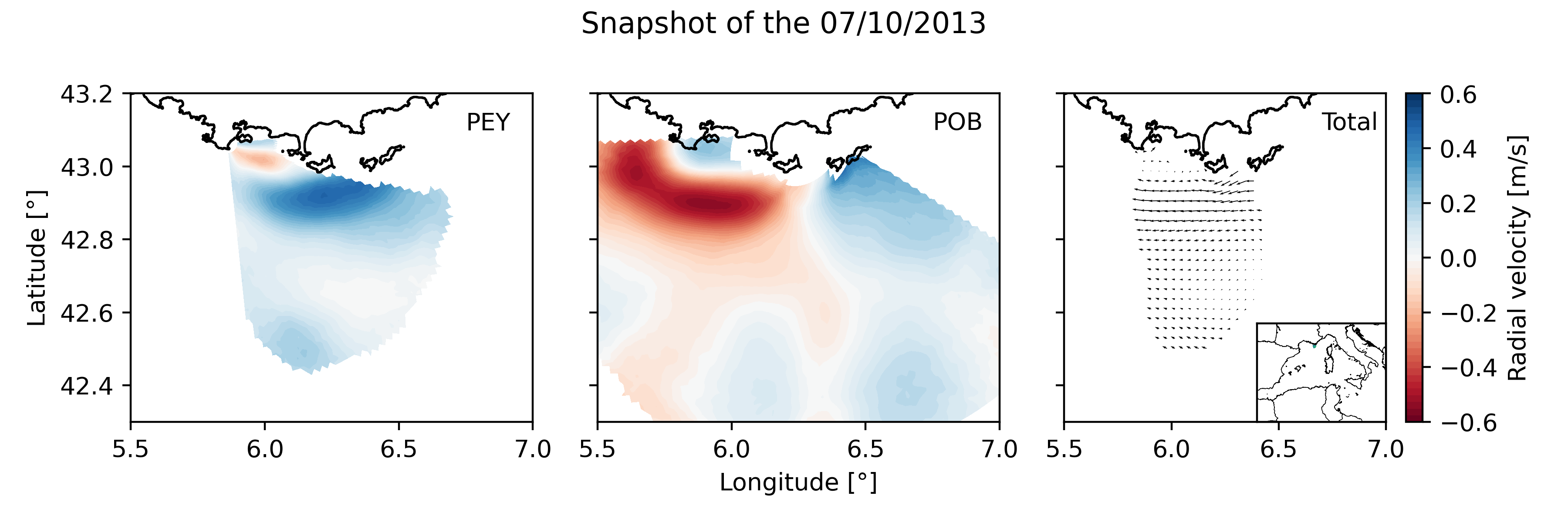
Daily High Frequency Radar (HFR) surface current data (radial velocity files and total velocity file) from 2 different stations located on the French Mediterranean coast (Toulon), spanning from January 2012 to December 2019. The radial datasets have been processed to remove outliers. Then, the gaps in the data have been filled using the DINEOF algorithm. The total velocity is then reconstructed from the filled radial velocity files, and projected onto a cartesian grid of 1km x 1km. The HFR data comes from two systems, one monostatic radar PEY (located at Fort Peyras, La Seyne sur mer), and one bistatic POB (emitter located at Cap Bénat - Bormes les Mimosas, and transmitter on Porquerolles Island). The HFR data is initially hourly sampled. To remove the outliers of the data, for each timestep, a Probability Density Function (PDF) is computed on the spatial gradient of each radial map. Pixels with a spatial gradient with a probability under 3% are removed. Additionnally, for each pixel, a PDF is computed on the temporal gradient of its whole timeseries. Timesteps with a temporal gradient that have a probability under 1% are then removed. Then we proceed to a preliminary temporal and spatial hole filling of the missing data. For the timeseries of each pixel, timesteps that are surrounded by valid values within 3 hours (i.e. 3 timesteps) are filled by a weighted linear interpolation. For each timestep, pixels of the map surrounded by values within 1 grid point are filled in the same way. The radial data is then daily averaged. The DINEOF algorithm (https://orbi.uliege.be/bitstream/2268/87104/1/IMDIS_alvera30sep.pdf) is run in a multivariate way (2 radial velocity files) using 50 EOF modes for the reconstruction. At some timesteps (shown by the flag variable of the file), the filling has not been possible, and the missing maps have been replaced by the temporal average radial map. The filled radial velocities are then locally interpolated onto a cartesian grid of 1km spatial resolution using a Weighted Least Square method. HF radar sites : - Peyras : 43°03'47.4"N, 5°51'40.3"E - Porquerolles (transmitter only): 42°58'59.0"N, 6°12'15.3"E - Bénat (receiver only): 43°05'31.5"N, 6°21'26.5"E EUROPEAN DIRECTORY OF MARINE ENVIRONMENTAL RESEARCH PROJECTS (EDMERP) : - SICOMAR PLUS(12402), IMPACT(12271), MOOSE(11574), and JERICO NEXT(12227) EQUIPEMENTS: - High Frequency Surface Wave radar WERA from HELZEL MESSTECHNIK PARAMETERS: - sea surface current Citation: Molcard, A., & Bourg, N. (2021). HF RADAR - French Riviera (Mediterranean Institute of Oceanography) - daily surface currents filled with DINEOF [Data set]. MIO UMR 7294 CNRS. https://doi.org/10.34930/9263C4DF-4F55-4C5A-B183-C40EE1D844B1
 OSU Pytheas - Data Catalog
OSU Pytheas - Data Catalog