5000
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-

The Health and Demographic Surveillance System (HDSS) in Niakhar, a rural area of Senegal, is located 135 km east of Dakar. This HDSS has been set up in 1962 by the Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD) to face the shortcomings of the civil registration system and provide demographic indicators. Some 65 villages were followed annually in the Niakhar area from 1962 to 1969. The study zone was reduced to eight villages from 1969 to 1983, and from then on the HDSS was extended to include 22 other villages, covering a total of 30 villages for a population estimated at 45,000 in December 2013. Thus 8 villages have been under demographic surveillance for almost 50 years and 30 villages for 30years. Vital events, migrations, marital changes, pregnancies, immunization are routinely recorded (every four months). The database also includes epidemiological, economic and environmental information coming from specific surveys. Data were collected through annual rounds from 1962 to 1987; rounds became weekly from 1987 to 1997; routine visits were conducted every three months between 1997and 2007 and every four months since then. The current objectives are 1) to obtain a long-term assessment of demographic and socio-economic indicators necessary for bio-medical and social sciences research, 2) to keep up epidemiological and environmental monitoring, 3) to provide a research platform for clinical and interdisciplinary research (medical, social and environmental sciences). Research projects during the last 5 years are listed in Table 2. The Niakhar HDSS has institutional affiliation with the Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD, formerly ORSTOM). * Niakhar HDSS INDEPTH Core Dataset 1984-2016 (Release 2018). Provided by the INDEPTH Network Data Repository. http://indepth-ishare.org/index.php/catalog/132 * DOI : 10.7796/INDEPTH.SN013.CMD2016.v1 * https://doi.org/10.7796/INDEPTH.SN013.CMD2016.v1
-
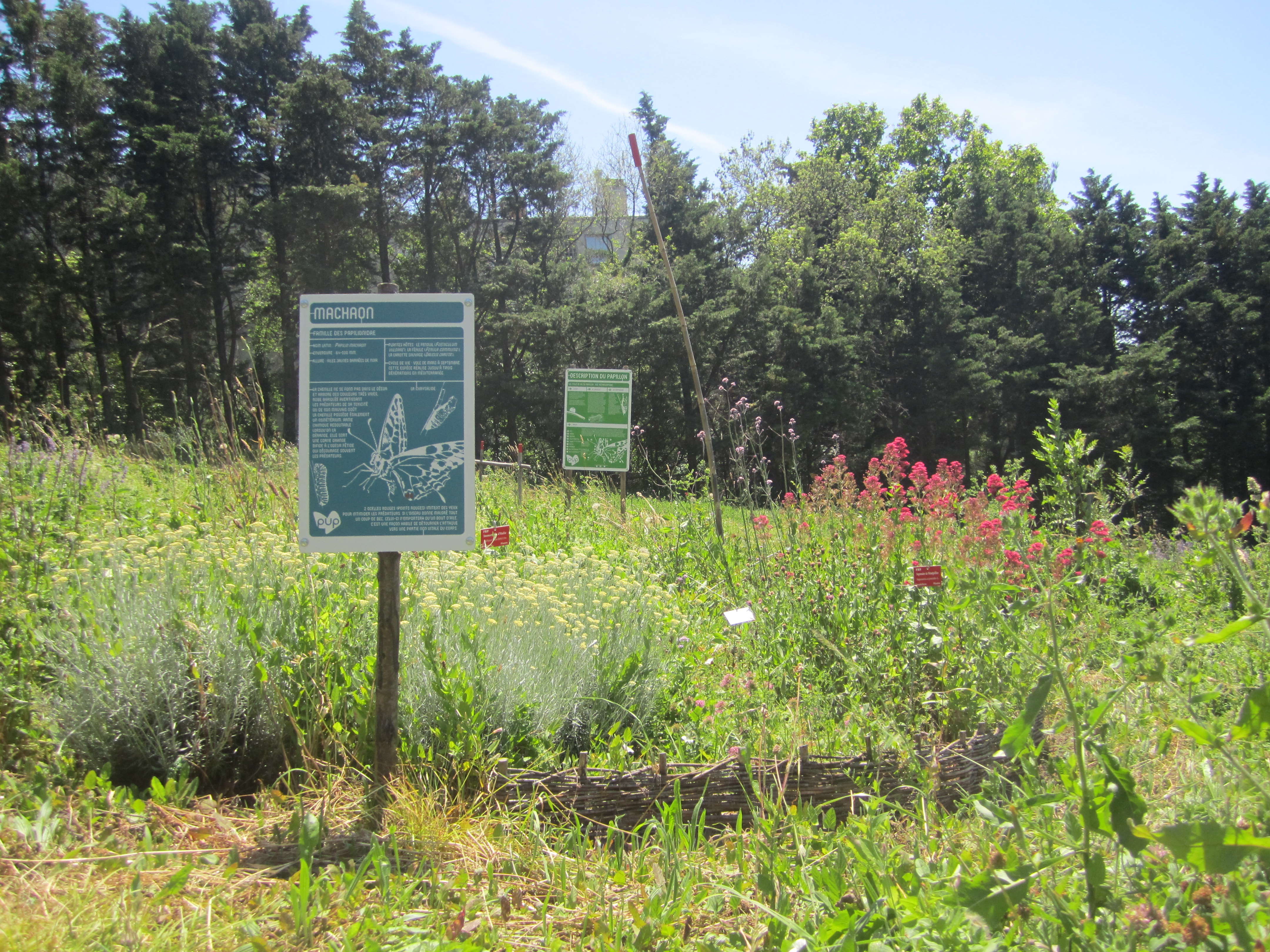

Communities of Rhopalocera (Lepidoptera) butterflies in 24 urban parks in Marseille Sampling of Rhopalocera communities: 7 to 12 transects in each of 24 urban parks in Marseille every 2 years since 2008. Increasing numbers of cities are currently developing sustainable policies aimed at promoting urban biodiversity and ecological dynamics through the planning of green networks and the implementation of more sustainable management practices. These human activities can strongly influence environmental factors on which the organization of ecological communities at different scales depends. Thus, it is of fundamental importance to understand the relative impact of local management, green space design and landscape features on the distribution and the abundance of species in urban areas. On the basis of 2 years of butterfly surveys in urban public parks within an extensive Mediterranean metropolitan area, Marseille (South-East France), the aim of this paper is to provide a better understanding of the effect of these three environmental scales (plot, park, landscape) on the composition and organization of species assemblages. Using variation partitioning and nestedness analysis on ecological data aggregated at plot-level and park-level respectively, we demonstrate the preponderant effect of landscape scale features on urban butterfly assemblages. Our results also highlight an important co-variation of plot management, park layout and urban landscape features, in their interaction with the community structure of urban butterflies. Although there is no significant species-area relationship, significantly nested patterns arise in species composition. Selective colonization appears as a driving force constraining the constitution of species assemblages within the city. However, a prospective study on adjacent more natural areas suggests that biotic limitations, interspecific competition and habitat filtering may play an important role if a larger portion of the urbanization gradient is explored, which remains to be investigated.
-
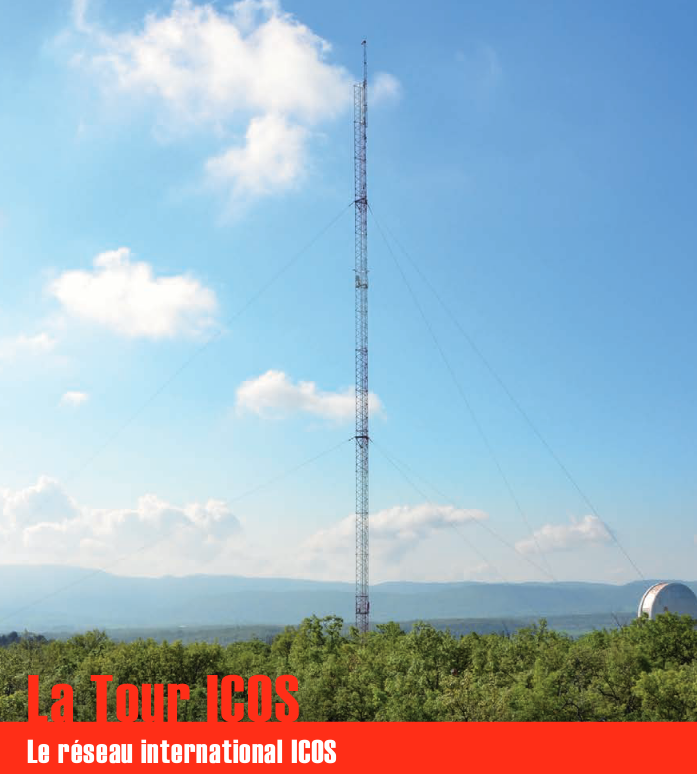

Une infrastructure de recherche européenne de mesure des concentrations atmosphériques des gaz à effet de serre et des flux de carbone sur les écosystèmes et l’océan. La tour ICOS (pour Integrated Carbon Observation System) installée à l'Observatoire de Haute Provence (OHP), haute de 100 m est une antenne régionale du dispositif permettant d’étudier la place de la forêt méditerranéenne dans le bilan de carbone. Elle est équipée d’instruments à trois niveaux (10, 50, 100 m). Le réseau est doté de 3 types de stations réparties sur le territoire : continentales, côtières et de montagne. Chacune de ces stations mesure les paramètres suivants : * température, direction et vitesse du vent, pression atmosphérique, humidité * CO2, CH4, CO, H2O * hauteur de couche limite atmosphérique (lidar) Les objectifs scientifiques de ce programme européen sont de : * tracer les flux de carbone en Europe et dans les régions adjacentes par observation des écosystèmes, de l'atmosphère et des océans à travers des réseaux intégrés, * fournir les observations à long terme nécessaires pour comprendre l'état présent et prévoir le comportement du carbone global et des émissions des gaz à effet de serre, * surveiller et évaluer l'efficacité de la séquestration du carbone et/ou de la réduction des émissions de gaz à effet de serre sur la composition globale de l'atmosphère, en prenant en compte les sources et les puits par région géographique et par secteur d'activité. L'infrastructure ICOS permet d'accueillir des chercheurs pour des campagnes de recherches
-
L’île de Bagaud, réserve intégrale du Parc National de Port Cros (PNPC), fait actuellement l‘objet d’un programme décennal de restauration écologique en vue de la préservation de son patrimoine naturel. Cette restauration consiste à contrôler deux espèces exotiques envahissantes : le rat noir (Rattus rattus) et la griffe de sorcière (Carpobrotus sp.). Débuté en 2010, ce programme permet l’étude de plusieurs groupes taxonomiques avant (2010-2011) et après contrôle (2013-2019) : (1) la flore, (2) les arthropodes épigés et les insectes volants, (3) les squamates, (4) les oiseaux terrestres nicheurs et (5) les oiseaux marins nicheurs. Ce projet fédère une large communauté d’acteurs académiques et non-académiques autour d’un objectif commun : contrôler et si possible éradiquer les espèces invasives de la réserve intégrale et suivre la résilience des groupes taxonomiques cités ci-dessus. Partenaires pour le suivi et l’analyse des données : IMBE, PNPC, CBNMed, association Reptil’Var, association DREAM et LPO. Autres partenaires : PIM, INRA, Conservatoire du Littoral, Domaine du Rayol, Naturoscope, UE, Natura2000, TLV, Région Sud, Naturalia Consultants en Environnement.
-
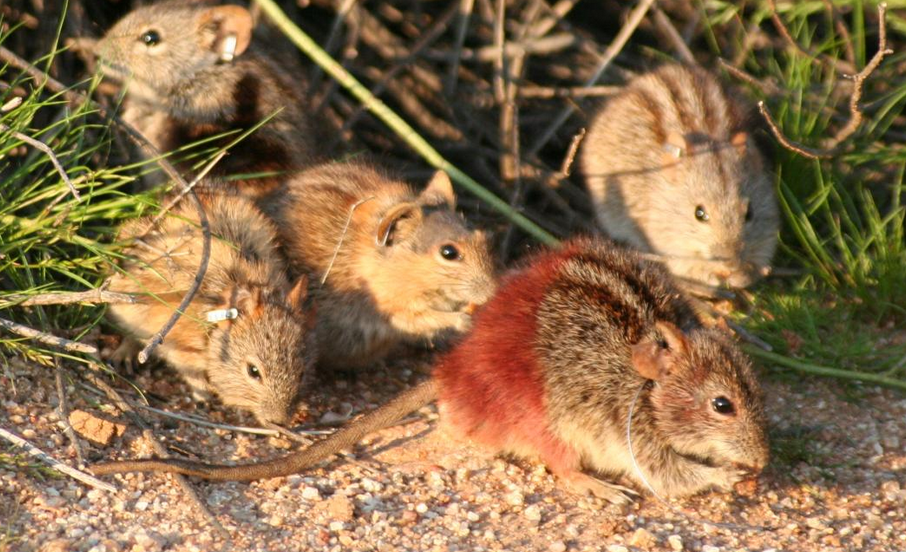

Suivi longitudinal sur 9 sites de terrain au Sénégal de l’observatoire ObsMiCE Paramètres mesurés: - détermination spécifique ; - indices d’abondance ; - données morphométriques, - estimation de l’âge, - paramètres de reproduction indicateurs de la dynamique des populations animales ; - prélèvements de tissus, d’ectoparasites et d’endoparasites ; - données environnementales ; - prévalence de parasites et pathogènes
-

JULIO (Judicious Location for Intrusions Observations) mooring is located close to the 100 m-deep isobath (around 5.25°E and 43.13°N), offshore Marseille. With its bottom-moored (300kHz) ADCP, it enables measuring horizontal currents (every 4 m and every ½ h) through the water column, and among others, identifying periods of exchange between the Northern Current and the continental shelf. It is one crucial component in the study of the coastal-offshore gradient from Marseille to the MOOSE 42°N5°E station, and potential covariances with the MIO radar and other MIO or international observing systems, as well as with the SOMLIT site (including also an ADCP) in the bay of Marseille. Moreover, with a bottom CTD, it can detect environmental anomalies in classical hydrographic data, useful for oceanographers. As one of the rare station at the interface between the continental shelf and offshore, it will allow to observe the long-term evolution of the Northern Current in the context of climate change and anthropogenic pressure, and its potential varying impact on the Gulf of Lion. The data are of course also crucial for modellers. Moreover they show a great potential when supplementing other MOOSE data (glider and radar). Timeserie #3 : - JULIO 3 - 17/07/2014 to 10/04/2015; JULIO (Judicious Location for Intrusions Observations) est situé à proximité de l'isobathe de 100 m de profondeur (environ 5,25°E et 43,13°N), au large de Marseille. Grâce à son ADCP (300 kHz), il permet de mesurer les courants horizontaux (tous les 4 m et toutes les ½ h) à travers la colonne d'eau et, entre autres, d'identifier les périodes d'échange entre le courant du Nord et le plateau continental. Il s'agit d'un élément crucial dans l'étude du gradient littoral-offshore de Marseille à la station MOOSE 42°N5°E, et des covariances potentielles avec le radar MIO et autres systèmes d'observation MIO ou internationaux, ainsi qu'avec le site SOMLIT (incluant également un ADCP) dans la baie de Marseille. De plus, avec un CTD de fond, il peut détecter les anomalies environnementales dans les données hydrographiques classiques, utiles aux océanographes. En tant qu'une des rares stations à l'interface entre le plateau continental et le large, elle permettra d'observer l'évolution à long terme du courant du Nord dans le contexte du changement climatique et de la pression anthropique, et son impact potentiel variable sur le Golfe du Lion. Les données sont bien sûr également cruciales pour les modélisateurs. De plus, ils présentent un grand potentiel en complément d'autres données MOOSE (planeur et radar). Série temporelle #3 : - JULIO 3 - 17/07/2014 to 10/04/2015;
-

JULIO (Judicious Location for Intrusions Observations) mooring is located close to the 100 m-deep isobath (around 5.25°E and 43.13°N), offshore Marseille. With its bottom-moored (300kHz) ADCP, it enables measuring horizontal currents (every 4 m and every ½ h) through the water column, and among others, identifying periods of exchange between the Northern Current and the continental shelf. It is one crucial component in the study of the coastal-offshore gradient from Marseille to the MOOSE 42°N5°E station, and potential covariances with the MIO radar and other MIO or international observing systems, as well as with the SOMLIT site (including also an ADCP) in the bay of Marseille. Moreover, with a bottom CTD, it can detect environmental anomalies in classical hydrographic data, useful for oceanographers. As one of the rare station at the interface between the continental shelf and offshore, it will allow to observe the long-term evolution of the Northern Current in the context of climate change and anthropogenic pressure, and its potential varying impact on the Gulf of Lion. The data are of course also crucial for modellers. Moreover they show a great potential when supplementing other MOOSE data (glider and radar). Timeserie #2: - JULIO 2 - 17/09/2013 to 28/03/2014; JULIO (Judicious Location for Intrusions Observations) est situé à proximité de l'isobathe de 100 m de profondeur (environ 5,25°E et 43,13°N), au large de Marseille. Grâce à son ADCP (300 kHz), il permet de mesurer les courants horizontaux (tous les 4 m et toutes les ½ h) à travers la colonne d'eau et, entre autres, d'identifier les périodes d'échange entre le courant du Nord et le plateau continental. Il s'agit d'un élément crucial dans l'étude du gradient littoral-offshore de Marseille à la station MOOSE 42°N5°E, et des covariances potentielles avec le radar MIO et autres systèmes d'observation MIO ou internationaux, ainsi qu'avec le site SOMLIT (incluant également un ADCP) dans la baie de Marseille. De plus, avec un CTD de fond, il peut détecter les anomalies environnementales dans les données hydrographiques classiques, utiles aux océanographes. En tant qu'une des rares stations à l'interface entre le plateau continental et le large, elle permettra d'observer l'évolution à long terme du courant du Nord dans le contexte du changement climatique et de la pression anthropique, et son impact potentiel variable sur le Golfe du Lion. Les données sont bien sûr également cruciales pour les modélisateurs. De plus, ils présentent un grand potentiel en complément d'autres données MOOSE (planeur et radar). Série temporelle #2 : - JULIO 2 - 17/09/2013 to 28/03/2014;
-

Wind is generated from left to right by an imposed constant horizontal pressure gradient. The initial wind field is disturbed by small random variations so as to produce a turbulent field. Withouth the perturbations, a viscous solution would be found. The numerical resolution technique used is based on finite differences, applied to a structured mesh. The Continuity and Navier-Stokes equations are solved with the well-known half time-step method, in which the Poisson equation is solved over the entire domain at each time iteration. As of 17 March 2022, the code version is DNS_2D_for_Teaching-v1.0.0. The code is written in C language. A GUI (Graphical User Interface) is available as an executable file "sdiapp.exe" that can be run under most versions of Microsoft Windows. Please just make sure to check the 'graph' box before clicking on the launch button, to have the visual experience. On the GUI, two graphs give an overview of the real time simulation. The top graph shows the 2D (x,z) vorticity, while the bottom graph shows the wind speed. The colour bars are not shown, but they are classical tables in which blue means small values, while red colours denote large values. The authors of this code version are Francis Vivat (LATMOS UMR CNRS 8190) and Denis Bourras (MIO UMR 7294). The code is distributed freely and comes with no garantees. It was mainly designed for educational purposes. Please note that the rules of use must follow the CeCILL-C FREE SOFTWARE LICENSE AGREEMENT included in the distribution. Any return is welcomed and encouraged, please contact francis.vivat@latmos.ipsl.fr or denis.bourras@mio.osupytheas.fr. Citation: Vivat, F., & Bourras, D., (2023). DNS_2D_for_Education [Application].
-
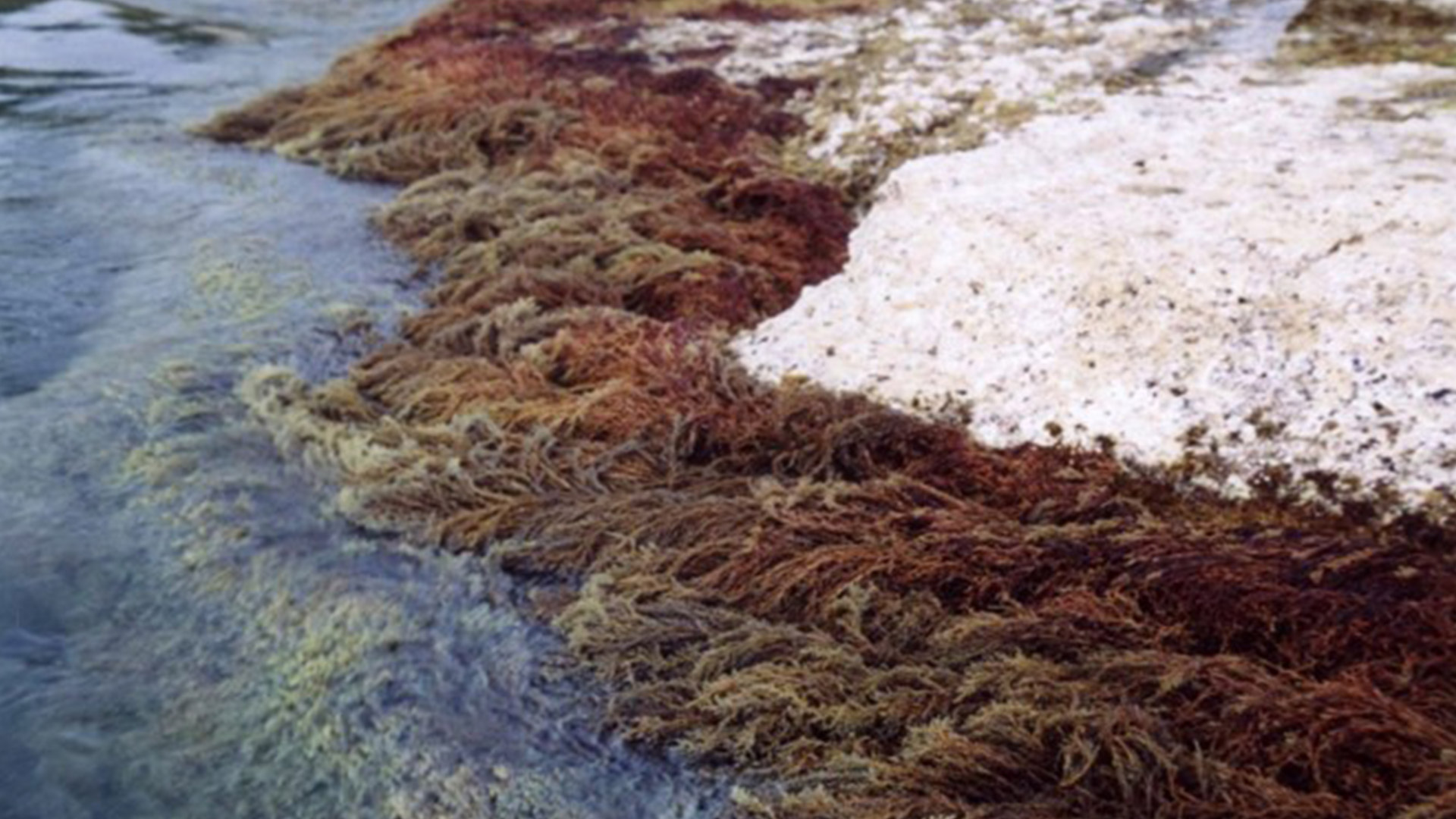

CARLIT : Évaluation de l’état écologique du littoral rocheux méditerranéen français – Descripteur ‘Macroalgue’ de la Directive Européenne Cadre sur l’Eau Dans le cadre du contrôle de surveillance DCE-Bassin Rhône côtier Méditerranée, la mise en œuvre du descripteur ‘Macroalgue’ a été mise en place depuis le printemps 2007 en utilisant la méthode CARLIT. Les communautés rocheuses des étages médio- et infralittoraux (frange supérieur de l’étage infralittoral souvent émergée), la géomorphologie et la nature de la roche ont été cartographiées à l’échelle 1/2 500ème. Un niveau de sensibilité écologique face aux perturbations sur une échelle de 1 (peu sensible) à 20 (très sensible) est attribué à chaque communauté. Les communautés ayant les niveaux de sensibilité les plus forts représentent les communautés climax de la zone littorale. Par une analyse géo-référencée, un indice de qualité environnementale est calculé, et permet ainsi de déterminer, pour chaque masse d’eau, un statut écologique établi suivant les critères de la Directive Cadre Européenne sur l’Eau. Les littoraux sédimentaires sont ignorés à l’exception des baies naturelles très fermées où les phanérogames peuvent être abondantes, ainsi que l’intérieur des ports et des marinas. Ces deux dernières zones étant trop perturbées, elles nécessitent l’utilisation d’autres indices comme par exemple l’analyse de l’eau. L’intégralité des côtes rocheuses françaises méditerranéennes a été cartographie (depuis 2007). La méthode CARLIT (CARtographie LITtorale) développée par Ballesteros et al., 2007 et modifié par Blanfuné et al., 2017, consiste à mesurer l'abondance et la distribution des communautés ou espèces de macroalgues dominantes présentes sur les substrats rocheux de l’étage médiolittoral et de l'horizon supérieur de l’étage infralittoral (0-50 cm de profondeur) en fonction de la géomorphologie de la côte (présence de falaise supérieure à 15 m de hauteur) et de la nature du substrat (naturel, artificiel, etc.). L'abondance des communautés est cartographiée à partir d’une petite embarcation longeant la côte au plus près du littoral et à 4-5 km/h. La méthode ne s’applique donc pas à des masses d’eau dont la côte est sableuse, où le descripteur macroalgues n’est pas pertinent. Par une analyse géoréférencée, un indice de qualité environnementale (EQR) est calculé, et permet ainsi de déterminer, pour chaque masse d’eau, un statut écologique (ES) établi suivant les critères de la Directive Cadre Européenne sur l’Eau. Une deuxième vague d’évaluation a commencé depuis 2012.
-
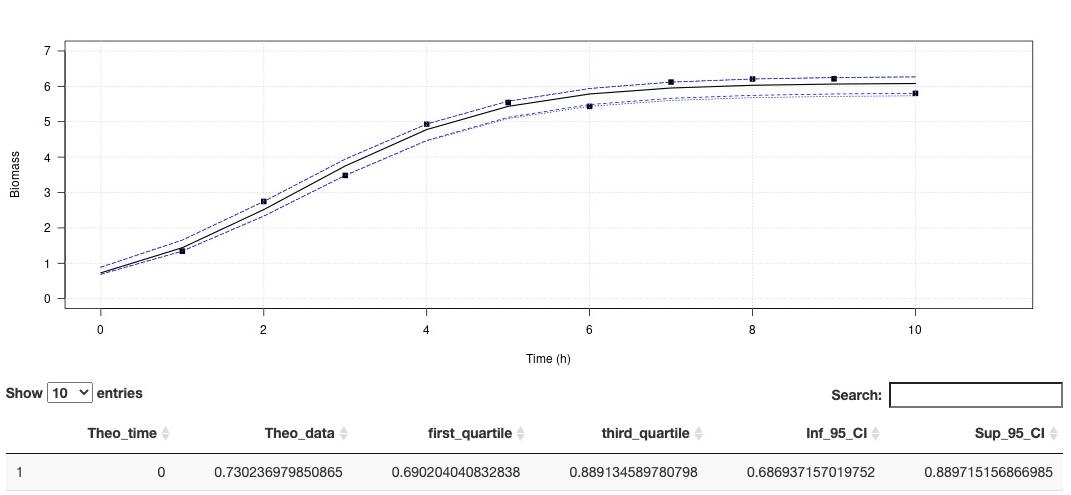
Environmental conditions are a set of physical and biological variables that define an ecosystem. Microorganisms with higher generation times than more complex multicellular organisms are more sensitive to changing environmental conditions. Therefore, microbial growth curves are an important and simple way to understand how environmental conditions affect microorganisms. Growth curves are used in a variety of biological applications. Traditionally in microbiology, the maximum growth rate (µmax) is calculated by fitting a linear model on data of the exponential growth phase. This method is simple to implement, and robust if the exponential phase contains many points. However, this method is very limiting when the curve is described with few points, as we have seen with experiments under high pressure conditions. In order to overcome this limit, recurrent in biology, we propose to use models to estimate growths parameters. Modeling has existed for many years to describe the growth behavior of microorganisms under variable physical and chemical conditions (Zwietering et al., 1990). Here we propose a ready-to-use application that do not require any special coding skills and allow retrieving several essential parameters describing microbial growth. his app aims at estimating the growth rate and maximum cells density using non-linear regression. The method is detailled in Martini et al. (2013). A demo dataset is available in "Download a demo dataset", you can save it in your computer and load it using "Browse", or you can also browse your own dataset. On Plot panel, it is possible to set axes labels, axes range and Smooth. Smooth parameter can compute theorical (downloadable) for to use with other activities. In order to run this application, you have to format your dataset with tabulation separators. Also, remove all spaces in the dataset header (prefer to use "_" when needed). Organise your dataset so that there is only two arrays. The first one being the time and the second one, the cells density (e. g. optic density, cell number, biomass). This application proposes a method to perform a logistic regression to estimate growth rate as well as maximum cells density . Citation: Garel, M., Izard, L., Vienne, M., Nerini, D., Tamburini, C., Martini, S. (2021). R-shiny-microorganisms v2 : A ready-to-use logistic regression implemented in R shiny to estimate growth parameters of microorganisms [Data set]. MIO UMR 7294 CNRS. https://doi.org/10.34930/DC1DAF1C-09E3-4829-8878-91D0BF0E643E
 OSU Pytheas - Data Catalog
OSU Pytheas - Data Catalog