asNeeded
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-

OBJECTIF – Mesures des flux de matières d’origine atmosphérique en mer Méditerranée dans le cadre du réseau MOOSE Mesures en réseau avec cap Béar et cap ferrat Le milieu marin est de plus en plus soumis à l’influence anthropique, très directement sur la frange littorale, mais également au large par les retombées atmosphériques qui peuvent se propager très loin. La Méditerranée étant une mer oligotrophe, c’est-à-dire pauvre en élément nutritifs, tout apport d’éléments peut être un facteur de développement biologique significatif. Par contre l’apport de contaminants et de polluants par voie atmosphérique peut être un facteur perturbant ou inhibant l’écosystème. Le site du Frioul offrant l’opportunité de quantité les retombées atmosphériques dans la zone côtière, le Service d’Observation du MIO a proposé d’utiliser ce site pour installer des collecteurs de retombées atmosphériques. Collecteur de retombées atmosphériques sèches et pluies (MTX Italia) installé sur une plateforme dans l’enceinte du sémaphore de Pomègues Un collecteur de type MTX permet de récupérer les retombées sèches et les retombées humides (pluies) séparément. Parallèlement, un système de pompage en continu des aérosols a été mise en place dans la pièce supérieure du sémaphore. Il est composé de pompes à vide reliées à un compteur qui aspire en continu l’air qui est filtré sur un filtre disposé à l’extérieur. La collecte des échantillons est assurée chaque semaine par un opérateur du MIO. Par ailleurs le MIO assure le traitement et l’analyse de la matière récoltée. Les éléments suivants, source de fertilisation du milieu marin sont déterminés : - Azote total - Phosphore total - Carbone total - Formes solubles de l’azote (nitrate, nitrite, ammonium) - Formes solubles du phosphore (orthophosphates) - Formes particulaires de l’azote, du phosphore et du carbone. SITE : Iles de Pomègues - Sémaphore du Frioul PROGRAMME DE RATTACHEMENT - Mediterranean Oceanic Observing System on Environment : MOOSE - Labellisation : SOERE - INSU - Financement : SOERE – INSU – Ville de Marseille RESPONSABLE LOCAL: - Patrick Raimbault DISPONIBLITE DES DONNEES : - Base de données SEDOO: http://mistrals.sedoo.fr/MOOSE/ PARTICIPANTS : - M. Fornier : collecte - V. Lagadec analyses chimiques - P. Raimbault : analyses élémentaires PARTENAIRES - MOOSE - CHARMEX- Ville de Marseille – Parc des îles du Frioul - OSU de Villefranche et de Banyuls
-

Point vector file representing the sampling sites of atmospheric particles on tree leaves. Sampling performed in 2005. Contact : Y. Noack (CEREGE).
-

The MANGEBAUX study was proposed and supported at the 2013 call for research project of the OHM Bassin minier de Provence organised within the context of the Labex DRIIHM (CNRS/INEE). The study evaluates the atmospheric particle emissions (PM 2.5) notably from the Mangegarri storage site and in particular its content in bauxite ore derivatives which are the majority of the material stored.
-

Assuming the huge progress achieved in public participatory geographic information system (PPGIS) techniques and its current research gaps, this study aims to explore differences in the perception of spatial distribution of ecosystem services supply and demand between different stakeholders through collaborative mapping. In this case the stakeholders selected included high influence stakeholder (with a high degree of interest on the ecosystem services' state and with an important influence into the environmental decision making process). Workshops took place in June 2013 in two regions of Andalusia; overall 29 participants were involved. Three ecosystem services were mapped (erosion control, water depuration and climate regulation).
-
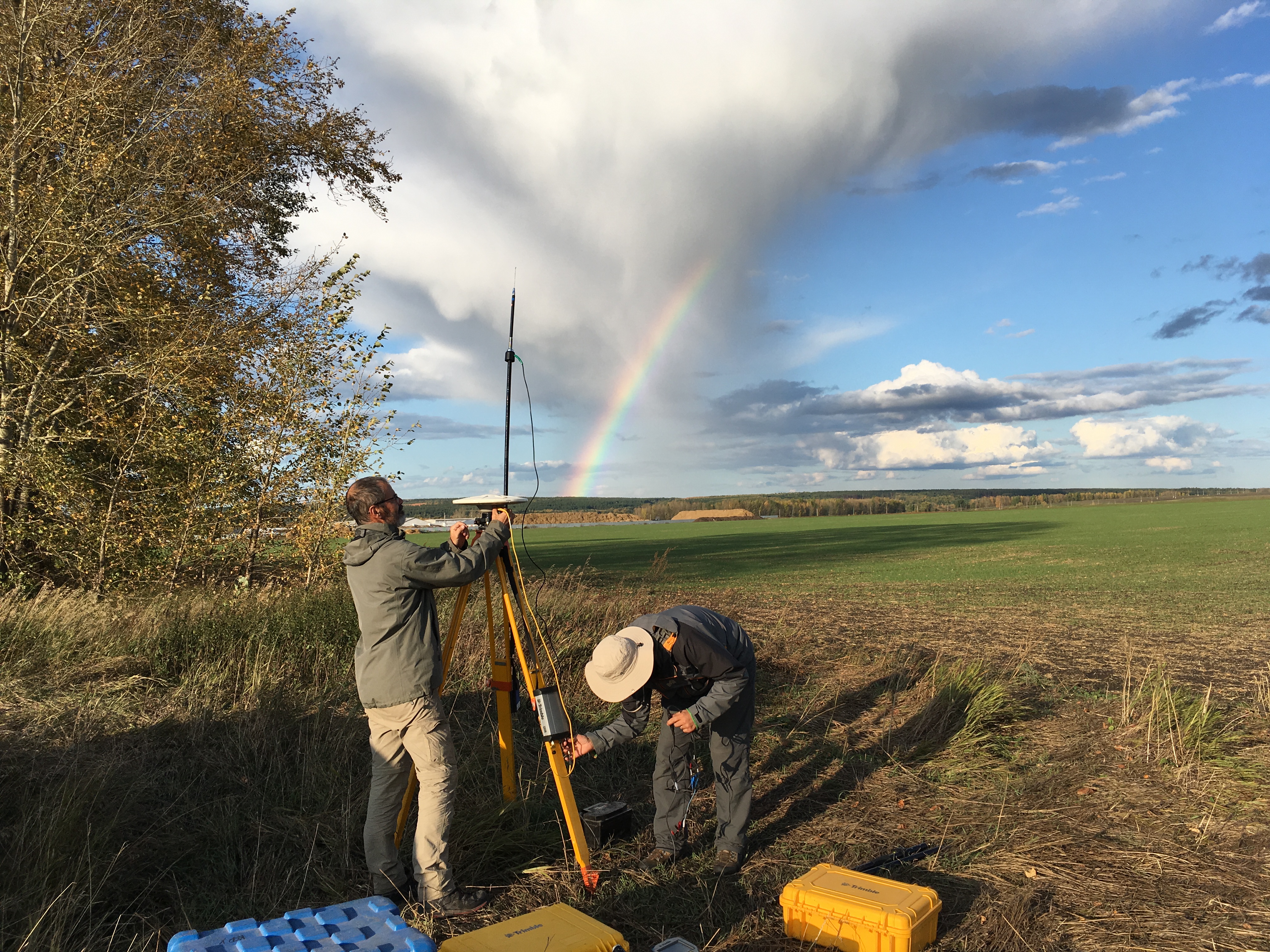

The GeoKarla dataset gathers geophysical and petrophysical data acquired over the Karla impact structure (Tatarstan, Russia). In September 2019, a field campaign on this eroded and buried structure was performed. Magnetic and gravity field observations were done, as well as geological mapping and sampling. Further petrophysical analyses in laboratory were performed on rock samples. All these data reveal - for the first time - a clear but unusual geophysical signature of the Karla impact structure. ==== acknowledgements ====== The associated research project was funded by: Russian Foundation for Basic Research RFBR grant no.18-55-5014 CNRS PRC French program Institutes/Participants: * Aix-Marseille Université, CNRS, IRD, INRAE, Aix-en-Provence, France Quesnel, Y., Rochette, P., Gattacceca, J., Uehara, M. * Institute of Geology and Petroleum Technologies, Kazan Federal University, 4/5 Kremlyovskaya Str., 420008, Kazan, Russia Bezaeva, N.S., Kuzina, D.M., Nasyrtdinov, B.M. * V.I. Vernadsky Institute of Geochemistry and Analytical Chemistry, Russian Academy of Scences, 19 Kosygin str., 119991 Moscow, Russia Bezaeva, N.S. , Badyukov, D.D. * Institute of Physics and Technology, Ural Federal University, 19 Mira Str., 620002 Ekaterinburg, Russia Bezaeva, N.S. Chareev, D.A. * Institute Experimental Mineralogy, Russian Academy of Science, 4 Academician Osipyan Str., 142432 Chernogolovka, Moscow Region, Russia Chareev, D.A. * National University of Science and Technology “MISiS”, 4 Leninsky Prospekt, 119049 Moscow, Russia Chareev, D.A. * Université de Montpellier, CNRS, Géosciences Montpellier, France Champollion, C.
-

Assuming the huge progress achieved in public participatory geographic information system (PPGIS) techniques and its current research gaps, this study aims to explore differences in the perception of spatial distribution of ecosystem services supply and demand between different stakeholders through collaborative mapping. In this case the stakeholders selected included low influence stakeholders (with a high degree of interest on the ecosystem services' state and with a low influence in environmental management). Workshops took place in June 2013 in two regions of Andalusia; overall 29 participants were involved. Two ecosystem services were mapped (freshwater and energy).
-

Study of the relationship between superficial water from lake and underground water, to constraint recharge mechanisms.
-
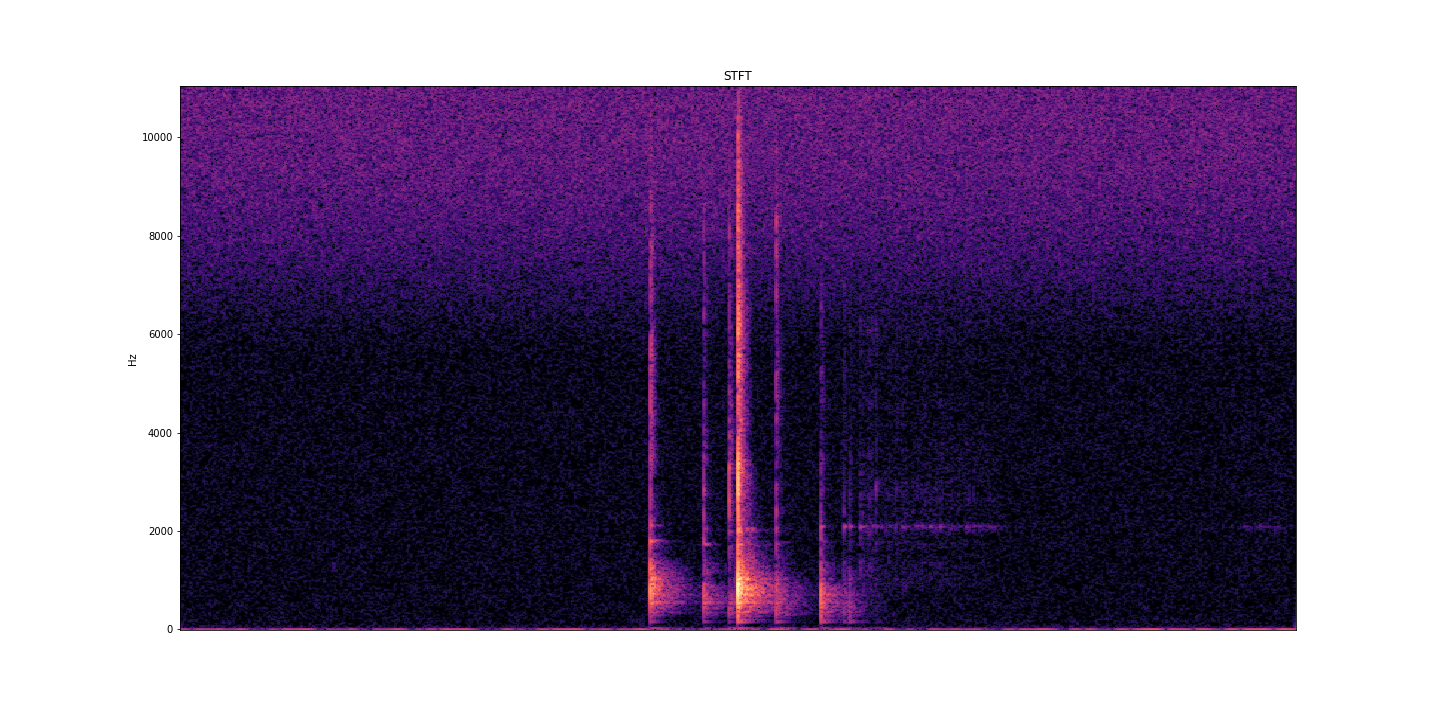
AcoustRivNN proposes to develop a system to estimate the flow and the granulometry of the sediment transport in a river from the acoustic pressure generated by the latter using methods from artificial intelligence. The estimation of the sediment flow carried by water, in rivers or estuaries, is a crucial issue for the management of the latter, allowing to carry out scientific studies, restoration or prevention projects, as well as operational works. Given the lack of effective methods to estimate the flow of sediment, the AcoustRivNN project proposes to provide a "proof of concept" by developing an original system based on deep learning to estimate the flow of coarse sediments from the simple acoustic pressure generated by the latter and measured by hydrophones. The originality of this project lies, in particular, in its interdisciplinary aspect proposing to adapt methods from artificial intelligence particularly effective in many applied fields. This project, which is part of the transversal axis 2: "Observations/information systems/modeling" of the ECCOREV federation, is structured in two phases: - Phase I proposes to build an acoustic database referenced in the laboratory necessary for the training of a neural network. - Phase II aims to develop a neural network model to characterize the acoustics of sediment flow. DOI: https://doi.org/10.34930/dc3225de-ef03-4134-927e-2347d75d8b41 Citation: Gassier, G., Michal, T., & Dussouillez, P. (2022). AcoustRivNN : flow and the granulometry of the sediment transport in a river from acoustic pressure [Data set]. CEREGE UMR 7330 CNRS. https://doi.org/10.34930/DC3225DE-EF03-4134-927E-2347D75D8B41
-

Assuming the huge progress achieved in public participatory geographic information system (PPGIS) techniques and its current research gaps, this study aims to explore differences in the perception of spatial distribution of ecosystem services supply and demand between different stakeholders through collaborative mapping. In this case the stakeholders selected included low influence stakeholders (with a high degree of interest on the ecosystem services' state and with a low influence in environmental management). Workshops took place in June 2013 in two regions of Andalusia; overall 29 participants were involved. Three ecosystem services were mapped (erosion control, water depuration and climate regulation).
-

Compilation of the post glacial RSL changes along the western mediterranean basin.
 OSU Pytheas - Data Catalog
OSU Pytheas - Data Catalog