dataset
Type of resources
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-

The Health and Demographic Surveillance System (HDSS) in Niakhar, a rural area of Senegal, is located 135 km east of Dakar. This HDSS has been set up in 1962 by the Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD) to face the shortcomings of the civil registration system and provide demographic indicators. Some 65 villages were followed annually in the Niakhar area from 1962 to 1969. The study zone was reduced to eight villages from 1969 to 1983, and from then on the HDSS was extended to include 22 other villages, covering a total of 30 villages for a population estimated at 45,000 in December 2013. Thus 8 villages have been under demographic surveillance for almost 50 years and 30 villages for 30years. Vital events, migrations, marital changes, pregnancies, immunization are routinely recorded (every four months). The database also includes epidemiological, economic and environmental information coming from specific surveys. Data were collected through annual rounds from 1962 to 1987; rounds became weekly from 1987 to 1997; routine visits were conducted every three months between 1997and 2007 and every four months since then. The current objectives are 1) to obtain a long-term assessment of demographic and socio-economic indicators necessary for bio-medical and social sciences research, 2) to keep up epidemiological and environmental monitoring, 3) to provide a research platform for clinical and interdisciplinary research (medical, social and environmental sciences). Research projects during the last 5 years are listed in Table 2. The Niakhar HDSS has institutional affiliation with the Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD, formerly ORSTOM). * Niakhar HDSS INDEPTH Core Dataset 1984-2016 (Release 2018). Provided by the INDEPTH Network Data Repository. http://indepth-ishare.org/index.php/catalog/132 * DOI : 10.7796/INDEPTH.SN013.CMD2016.v1 * https://doi.org/10.7796/INDEPTH.SN013.CMD2016.v1
-
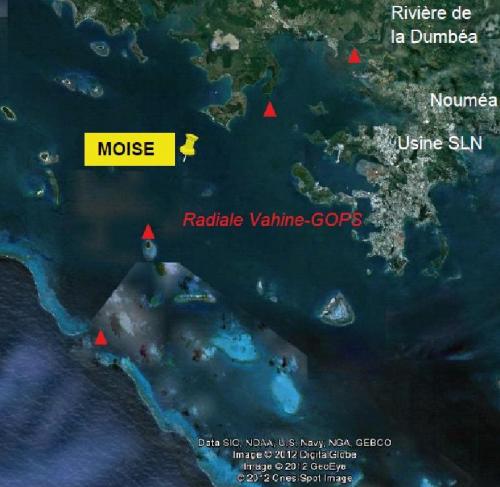
The MOISE project is part of a medium- and long-term approach to monitoring the coastal environment in New Caledonia. Initiated at the end of 2011, this monitoring is based on the installation of a fixed mooring with automatic physico-chemical, optical and biological measurement systems. This approach makes it possible to address the different scales of temporal variability characteristic of the dynamics and functioning of the lagoon ecosystem, including the daily scale. Since 2012, this high-frequency in situ monitoring has been supplemented by monthly monitoring with discrete measurements and vertical profiles over the entire water column; the parameters measured and the methods used are modelled on those of the SOMLIT network, with a view to MOISE's accreditation as an observation station. Medium and long term observation of the coastal environment in New Caledonia. Climatic variability in tropical zones. Evolution of the monthly, seasonal and interannual variability of the hydrological and biogeochemical characteristics of marine waters at a point located off the Bay of Dumbéa (N-NW of Noumea, New Caledonia) on a depth of 10m. Measurement of the impact of natural and anthropogenic forcings on the environment, study/quantification of the consequences of this variability, both natural and anthropogenic, on the structuring and functioning of the pelagic ecosystem, and in particular on the appearance of diazotrophic blooms. Validation of the images obtained by different ocean color sensors by monitoring the variations of the "water color" for an adjustment of the algorithms of calculation of the chlorophyll obtained from satellite reflectance. Possible measurements of the impact of the atmospheric plume of the SLN (Société Le Nickel = nickel treatment by pyrometallurgy) following preliminary work.
-
In 1985 the population and health observatory was established at Mlomp, in the region of Ziguinchor, in southern Senegal (see map). The objective was to complement the two rural population observatories then existing in the country, Bandafassi, in the south-east, and Niakhar, in the centre-west, with a third observatory in a region - the south-west of the country (Casamance) - whose history, ethnic composition and economic situation were quite different from those of the regions where the first two observatories were located. It was expected that measuring the demographic levels and trends on those three sites would provide better coverage of the demographic and epidemiological diversity of the country. Following a population census in 1984-1985, demographic events and causes of death have been monitored yearly. During the initial census, all women were interviewed concerning the birth and survival of their children. Since 1985, yearly censuses, usually conducted in January-February, have been recording demographic data, including all births, deaths, and migrations. The completeness and accuracy of dates of birth and death are cross-checked against those of registers of the local maternity ward (_95% of all births) and dispensary (all deaths are recorded, including those occurring outside the area), respectively. The study area comprises 11 villages with approximately 8000 inhabitants, mostly Diola. Mlomp is located in the Department of Oussouye, Region of Ziguinchor (Casamance), 500 km south of Dakar. On 1 January 2000 the Mlomp area included a population of 7,591 residents living in 11 villages. The population density was 108 people per square kilometre. The population belongs to the Diola ethnic group, and the religion is predominantly animist, with a large minority of Christians and a few Muslims. Though low, the educational level - in 2000, 55% of women aged 15-49 had been to school (for at least one year) - is definitely higher than at Bandafassi. The population also benefits from much better health infrastructure and programmes. Since 1961, the area under study has been equipped with a private health centre run by French Catholic nurses and, since 1968, a village maternity centre where most women give birth. The vast majority of the children are totally immunized and involved in a growth-monitoring programme (Pison et al.,1993; Pison et al., 2001) * DOI : 10.7796/INDEPTH.SN012.CMD2016.v1 * DOI : https://doi.org/10.7796/INDEPTH.SN012.CMD2016.v1
-

The Health and Demographic Surveillance System (HDSS) in Niakhar, a rural area of Senegal, is located 135 km east of Dakar. This HDSS has been set up in 1962 by the Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD) to face the shortcomings of the civil registration system and provide demographic indicators. Some 65 villages were followed annually in the Niakhar area from 1962 to 1969. The study zone was reduced to eight villages from 1969 to 1983, and from then on the HDSS was extended to include 22 other villages, covering a total of 30 villages for a population estimated at 45,000 in December 2013. Thus 8 villages have been under demographic surveillance for almost 50 years and 30 villages for 30years. Vital events, migrations, marital changes, pregnancies, immunization are routinely recorded (every four months). The database also includes epidemiological, economic and environmental information coming from specific surveys. Data were collected through annual rounds from 1962 to 1987; rounds became weekly from 1987 to 1997; routine visits were conducted every three months between 1997and 2007 and every four months since then. The current objectives are 1) to obtain a long-term assessment of demographic and socio-economic indicators necessary for bio-medical and social sciences research, 2) to keep up epidemiological and environmental monitoring, 3) to provide a research platform for clinical and interdisciplinary research (medical, social and environmental sciences). Research projects during the last 5 years are listed in Table 2. The Niakhar HDSS has institutional affiliation with the Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD, formerly ORSTOM). * Niakhar HDSS INDEPTH Core Dataset 1984-2016 (Release 2018). Provided by the INDEPTH Network Data Repository. www.indepth-network.og . * DOI : "10.7796/INDEPTH.SN011.CMD2016.v1" * https://doi.org/10.7796/INDEPTH.SN011.CMD2016.v1
 OSU Pytheas - Data Catalog
OSU Pytheas - Data Catalog