geoscientificInformation
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
Le projet interdisciplinaire UECOCOT vise à développer des outils d'aide à la gestion durable des activités minières afin de permettre la meilleure cohabitation possible entre dynamique naturelle des environnements (et leur capacité de résistance aux dommages et de résilience) et les activités humaines (industrielles ou non). L'objectif global du projet est de répondre à la question " comment adapter , à un coût socio-économique acceptable, les activités minières pour que leur impact reste compatible avec la durabilité des écosystèmes côtiers et littoraux". Pour atteindre un tel objectif, le projet UECOCOT repose sur une approche multi-sites ayant des impacts miniers différents. Dans le Pacifique sud, le site choisi est le lagon de Koné (Nouvelle-Calédonie) à proximité duquel s'est implanté une mine de nickel et touché par des apports de particules riches en éléments métalliques (Ni, Cr, Co, Mn) issues de l'altération des massifs miniers latéritiques développés sur des péridotites. C'est dans ce cadre qu'a eu lieu en février 2018 une campagnes océanographique multidisciplinaire dans le lagon de Koné dont l'objectif était d'acquérir des informations sur : i) les flux hydrodynamiques et biogéochimiques entre la côte, le lagon et l'océan et les connectivités au sein même du lagon, ii) l'état écologique du lagon et son fonctionnement End to End (hydro-bio-géochimique) , iii) les apports miniers directs ou indirects (avec un focus sur les métaux) et leur impact sur le fonctionnement biogéochimique. L'ensemble des résultats acquis doit permettre de valider un modèle numérique de biologie intégrant les aspects physiologiques et comportementaux des organismes (plancton et benthos) liés à la contamination du milieu et à la circulation hydrodynamique au sein du lagon. Il doit en particulier aboutir à une meilleure compréhension du rôle de la barrière récifale sur la régulation hydrodynamique et ainsi permettre d'affiner les prévisions en terme de contamination du lagon suite à une modification de la structure récifale sous l'effet conjugué de contraintes anthropiques et climatiques. Ce projet s'inscrit dans le réseau international AMEDEE (Activité Minière, Environnement, Développement Economique, Ethiques) qui regroupe les programmes de R&D de 40 institutions scientifiques (Colin, 2016)
-

This database is a compilation of published data from multiple publications dealing with seismotectonic studies of potentially active structures in Southeast France.
-

Review of soil physico-chemical variations between conventional and conservation agriculture in Mediterranean basin.
-

Compilation of the post glacial RSL changes along the western mediterranean basin.
-
Agroecological results
-

The Velingara dataset gathers geophysical and zircon data acquired in the Velingara circular depression (Senegal). In March 2022, a field campaign was performed in this depression, since it is thought to be an impact structure. Magnetic and gravity field observations were done, as well as sampling. Several zircon grains of sample VEL29A were analysed by LA-ICP-MS, given an age of 550 Ma.
-

The GeoKarla dataset gathers geophysical and petrophysical data acquired over the Karla impact structure (Tatarstan, Russia). In September 2019, a field campaign on this eroded and buried structure was performed. Magnetic and gravity field observations were done, as well as geological mapping and sampling. Further petrophysical analyses in laboratory were performed on rock samples. All these data reveal - for the first time - a clear but unusual geophysical signature of the Karla impact structure. ==== acknowledgements ====== The associated research project was funded by: Russian Foundation for Basic Research RFBR grant no.18-55-5014 CNRS PRC French program Institutes/Participants: * Aix-Marseille Université, CNRS, IRD, INRAE, Aix-en-Provence, France Quesnel, Y., Rochette, P., Gattacceca, J., Uehara, M. * Institute of Geology and Petroleum Technologies, Kazan Federal University, 4/5 Kremlyovskaya Str., 420008, Kazan, Russia Bezaeva, N.S., Kuzina, D.M., Nasyrtdinov, B.M. * V.I. Vernadsky Institute of Geochemistry and Analytical Chemistry, Russian Academy of Scences, 19 Kosygin str., 119991 Moscow, Russia Bezaeva, N.S. , Badyukov, D.D. * Institute of Physics and Technology, Ural Federal University, 19 Mira Str., 620002 Ekaterinburg, Russia Bezaeva, N.S. Chareev, D.A. * Institute Experimental Mineralogy, Russian Academy of Science, 4 Academician Osipyan Str., 142432 Chernogolovka, Moscow Region, Russia Chareev, D.A. * National University of Science and Technology “MISiS”, 4 Leninsky Prospekt, 119049 Moscow, Russia Chareev, D.A. * Université de Montpellier, CNRS, Géosciences Montpellier, France Champollion, C.
-
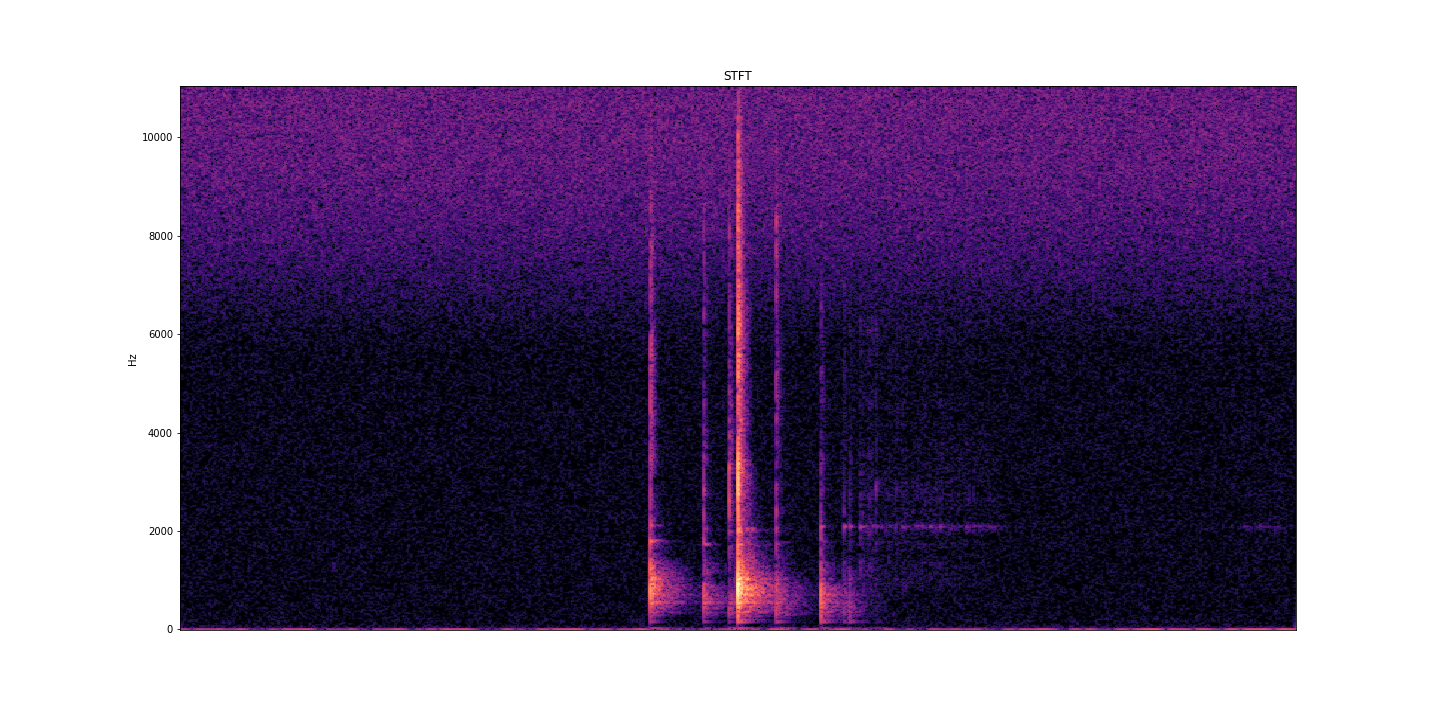
AcoustRivNN proposes to develop a system to estimate the flow and the granulometry of the sediment transport in a river from the acoustic pressure generated by the latter using methods from artificial intelligence. The estimation of the sediment flow carried by water, in rivers or estuaries, is a crucial issue for the management of the latter, allowing to carry out scientific studies, restoration or prevention projects, as well as operational works. Given the lack of effective methods to estimate the flow of sediment, the AcoustRivNN project proposes to provide a "proof of concept" by developing an original system based on deep learning to estimate the flow of coarse sediments from the simple acoustic pressure generated by the latter and measured by hydrophones. The originality of this project lies, in particular, in its interdisciplinary aspect proposing to adapt methods from artificial intelligence particularly effective in many applied fields. This project, which is part of the transversal axis 2: "Observations/information systems/modeling" of the ECCOREV federation, is structured in two phases: - Phase I proposes to build an acoustic database referenced in the laboratory necessary for the training of a neural network. - Phase II aims to develop a neural network model to characterize the acoustics of sediment flow. DOI: https://doi.org/10.34930/dc3225de-ef03-4134-927e-2347d75d8b41 Citation: Gassier, G., Michal, T., & Dussouillez, P. (2022). AcoustRivNN : flow and the granulometry of the sediment transport in a river from acoustic pressure [Data set]. CEREGE UMR 7330 CNRS. https://doi.org/10.34930/DC3225DE-EF03-4134-927E-2347D75D8B41
-

The Rochelec dataset gathers petrophysical and geoelectrical data from the Rochechouart impact structure (France). Since 2017, about 10 geophysical field campaigns were performed on this eroded structure. Among other techniques, geophysical downhole logging, electrical resistivity tomography and controlled-source audiomagnetotelluric data were acquired. In parallel, we measured the electrical resistivity and porosity of some core samples coming from drillings performed in fall 2017 at several sites of the impact structure. These multiscale electric data allows to better characterize the different lithologies outside the drilling sites, and their associated geometry. * Citation of this dataset Quesnel, Y., Sailhac, P., Lofi, J., Lambert, P., Rochette, P., Uehara, M. & Camerlynck, C. (2021). RochElec : Geoelectrical investigations on the Rochechouart impact structure (France) [Data set]. CEREGE UMR 7330 CNRS. https://doi.org/10.34930/BE0549D1-E876-49C5-B07F-BF04D398B25E * Publications linked with the dataset: Quesnel, Y., Sailhac, P., Lofi, J., Lambert, P., Rochette, P., Uehara, M. & Camerlynck, C. (2021). Rochechouart impact structure, France. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 22, e2021GC010036, https://doi.org/10.1029/2021GC010036
-
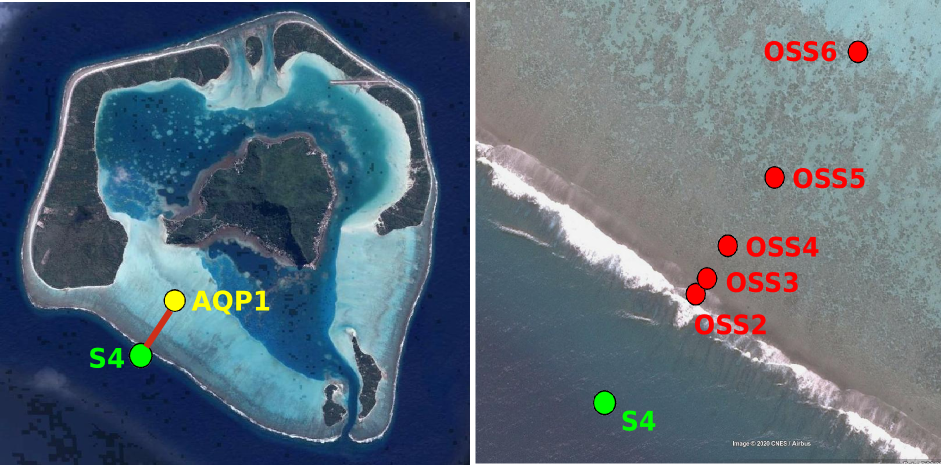
Maupiti ("the Stuck Twins'') is a diamond-shaped island located in the western part of the Society archipelago in French Polynesia. The present study focuses on the data recovered over a single cross-barrier transect located in the south-west barrier during the MAUPITI HOE field campaign, from 5 to 18 July 2018. The studied area is representative of the reef structure observed along the 4km-long southwestern barrier reef, showing an alongshore-uniform structure exposed to swell approaching with weak incident angles, a healthy reef colony. In the cross-barrier direction, the reef displays a clear partitioning of bottom roughness that ranges from low-crested compact structures at the reef crest to higher and sparser coral bommies on the backreef. The experimental setup was specifically designed to analyse and differentiate the dynamics over three roughness-contrasting sections found over the barrier reef. The scientific objectives of the project MAUPITI HOE are to understand the hydrodynamics of an archetypal reef-lagoon system of a high volcanic reef island. The physical functioning of the hydrosystem involves a fine coupling between water levels, waves (including wind, infragravity and VLF waves), currents and seabed structure (reef roughness). Four pressure sensors (OSS3, OSS4, OSS5, OSS6) have been deployed across the reef flat/ backreef, outside the surf zone. The bottom pressure is measured continuously at 10 Hz, and are converted into free surface elevation assuming hydrostaticity. An electrocurrent meter S4 provides the wave forcing while AQP1 is a velocity profiler providing the transports. The bed profile is obtained from the combination of (I) boat survey in the deeper part and (ii) high resolution GNSS RTK topography by feet. Two datasets are available: one is concerning the mean parameters linked to the reef barrier dynamics, and the second dataset is concerning the wave friction.
 OSU Pytheas - Data Catalog
OSU Pytheas - Data Catalog