ADCP
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-

JULIO (Judicious Location for Intrusions Observations) mooring is located close to the 100 m-deep isobath (around 5.25°E and 43.13°N), offshore Marseille. With its bottom-moored (300kHz) ADCP, it enables measuring horizontal currents (every 4 m and every ½ h) through the water column, and among others, identifying periods of exchange between the Northern Current and the continental shelf. It is one crucial component in the study of the coastal-offshore gradient from Marseille to the MOOSE 42°N5°E station, and potential covariances with the MIO radar and other MIO or international observing systems, as well as with the SOMLIT site (including also an ADCP) in the bay of Marseille. Moreover, with a bottom CTD, it can detect environmental anomalies in classical hydrographic data, useful for oceanographers. As one of the rare station at the interface between the continental shelf and offshore, it will allow to observe the long-term evolution of the Northern Current in the context of climate change and anthropogenic pressure, and its potential varying impact on the Gulf of Lion. The data are of course also crucial for modellers. Moreover they show a great potential when supplementing other MOOSE data (glider and radar). Timeserie #3 : - JULIO 3 - 17/07/2014 to 10/04/2015; JULIO (Judicious Location for Intrusions Observations) est situé à proximité de l'isobathe de 100 m de profondeur (environ 5,25°E et 43,13°N), au large de Marseille. Grâce à son ADCP (300 kHz), il permet de mesurer les courants horizontaux (tous les 4 m et toutes les ½ h) à travers la colonne d'eau et, entre autres, d'identifier les périodes d'échange entre le courant du Nord et le plateau continental. Il s'agit d'un élément crucial dans l'étude du gradient littoral-offshore de Marseille à la station MOOSE 42°N5°E, et des covariances potentielles avec le radar MIO et autres systèmes d'observation MIO ou internationaux, ainsi qu'avec le site SOMLIT (incluant également un ADCP) dans la baie de Marseille. De plus, avec un CTD de fond, il peut détecter les anomalies environnementales dans les données hydrographiques classiques, utiles aux océanographes. En tant qu'une des rares stations à l'interface entre le plateau continental et le large, elle permettra d'observer l'évolution à long terme du courant du Nord dans le contexte du changement climatique et de la pression anthropique, et son impact potentiel variable sur le Golfe du Lion. Les données sont bien sûr également cruciales pour les modélisateurs. De plus, ils présentent un grand potentiel en complément d'autres données MOOSE (planeur et radar). Série temporelle #3 : - JULIO 3 - 17/07/2014 to 10/04/2015;
-

JULIO (Judicious Location for Intrusions Observations) mooring is located close to the 100 m-deep isobath (around 5.25°E and 43.13°N), offshore Marseille. With its bottom-moored (300kHz) ADCP, it enables measuring horizontal currents (every 4 m and every ½ h) through the water column, and among others, identifying periods of exchange between the Northern Current and the continental shelf. It is one crucial component in the study of the coastal-offshore gradient from Marseille to the MOOSE 42°N5°E station, and potential covariances with the MIO radar and other MIO or international observing systems, as well as with the SOMLIT site (including also an ADCP) in the bay of Marseille. Moreover, with a bottom CTD, it can detect environmental anomalies in classical hydrographic data, useful for oceanographers. As one of the rare station at the interface between the continental shelf and offshore, it will allow to observe the long-term evolution of the Northern Current in the context of climate change and anthropogenic pressure, and its potential varying impact on the Gulf of Lion. The data are of course also crucial for modellers. Moreover they show a great potential when supplementing other MOOSE data (glider and radar). Timeseries : - JULIO 1 - 12/02/2012 -> 23/10/2012, every 4 minutes ; - JULIO 2 - 26/09/2013 -> 28/03/2014, every 4 minutes ; - JULIO 3 - 17/07/2014 -> 10/04/2015, every 4 minutes ; - JULIO 4 - 07/12/2020 -> 21/08/2021, every 5 minutes ; - JULIO 5 - 01/09/2021 -> 23/06/2022, every 4 minutes ; JULIO (Judicious Location for Intrusions Observations) est situé à proximité de l'isobathe de 100 m de profondeur (environ 5,25°E et 43,13°N), au large de Marseille. Grâce à son ADCP (300 kHz), il permet de mesurer les courants horizontaux (tous les 4 m et toutes les ½ h) à travers la colonne d'eau et, entre autres, d'identifier les périodes d'échange entre le courant du Nord et le plateau continental. Il s'agit d'un élément crucial dans l'étude du gradient littoral-offshore de Marseille à la station MOOSE 42°N5°E, et des covariances potentielles avec le radar MIO et autres systèmes d'observation MIO ou internationaux, ainsi qu'avec le site SOMLIT (incluant également un ADCP) dans la baie de Marseille. De plus, avec un CTD de fond, il peut détecter les anomalies environnementales dans les données hydrographiques classiques, utiles aux océanographes. En tant qu'une des rares stations à l'interface entre le plateau continental et le large, elle permettra d'observer l'évolution à long terme du courant du Nord dans le contexte du changement climatique et de la pression anthropique, et son impact potentiel variable sur le Golfe du Lion. Les données sont bien sûr également cruciales pour les modélisateurs. De plus, ils présentent un grand potentiel en complément d'autres données MOOSE (planeur et radar). Série temporelle #1: - JULIO 1 - 12/02/2012 -> 23/10/2012, toutes les 4 minutes ; - JULIO 2 - 26/09/2013 -> 28/03/2014, toutes les 4 minutes ; - JULIO 3 - 17/07/2014 -> 10/04/2015, toutes les 4 minutes ; - JULIO 4 - 07/12/2020 -> 21/08/2021, toutes les 5 minutes ; - JULIO 5 - 01/09/2021 -> 23/06/2022, toutes les 4 minutes ;
-

JULIO (Judicious Location for Intrusions Observations) mooring is located close to the 100 m-deep isobath (around 5.25°E and 43.13°N), offshore Marseille. With its bottom-moored (300kHz) ADCP, it enables measuring horizontal currents (every 4 m and every ½ h) through the water column, and among others, identifying periods of exchange between the Northern Current and the continental shelf. It is one crucial component in the study of the coastal-offshore gradient from Marseille to the MOOSE 42°N5°E station, and potential covariances with the MIO radar and other MIO or international observing systems, as well as with the SOMLIT site (including also an ADCP) in the bay of Marseille. Moreover, with a bottom CTD, it can detect environmental anomalies in classical hydrographic data, useful for oceanographers. As one of the rare station at the interface between the continental shelf and offshore, it will allow to observe the long-term evolution of the Northern Current in the context of climate change and anthropogenic pressure, and its potential varying impact on the Gulf of Lion. The data are of course also crucial for modellers. Moreover they show a great potential when supplementing other MOOSE data (glider and radar). Timeserie #6 : - JULIO 6 - 24/06/2022 to 22/06/2023; JULIO (Judicious Location for Intrusions Observations) est situé à proximité de l'isobathe de 100 m de profondeur (environ 5,25°E et 43,13°N), au large de Marseille. Grâce à son ADCP (300 kHz), il permet de mesurer les courants horizontaux (tous les 4 m et toutes les ½ h) à travers la colonne d'eau et, entre autres, d'identifier les périodes d'échange entre le courant du Nord et le plateau continental. Il s'agit d'un élément crucial dans l'étude du gradient littoral-offshore de Marseille à la station MOOSE 42°N5°E, et des covariances potentielles avec le radar MIO et autres systèmes d'observation MIO ou internationaux, ainsi qu'avec le site SOMLIT (incluant également un ADCP) dans la baie de Marseille. De plus, avec un CTD de fond, il peut détecter les anomalies environnementales dans les données hydrographiques classiques, utiles aux océanographes. En tant qu'une des rares stations à l'interface entre le plateau continental et le large, elle permettra d'observer l'évolution à long terme du courant du Nord dans le contexte du changement climatique et de la pression anthropique, et son impact potentiel variable sur le Golfe du Lion. Les données sont bien sûr également cruciales pour les modélisateurs. De plus, ils présentent un grand potentiel en complément d'autres données MOOSE (planeur et radar). Série temporelle #6 : - JULIO 6 - 24/06/2022 to 22/06/2023;
-

JULIO (Judicious Location for Intrusions Observations) mooring is located close to the 100 m-deep isobath (around 5.25°E and 43.13°N), offshore Marseille. With its bottom-moored (300kHz) ADCP, it enables measuring horizontal currents (every 4 m and every ½ h) through the water column, and among others, identifying periods of exchange between the Northern Current and the continental shelf. It is one crucial component in the study of the coastal-offshore gradient from Marseille to the MOOSE 42°N5°E station, and potential covariances with the MIO radar and other MIO or international observing systems, as well as with the SOMLIT site (including also an ADCP) in the bay of Marseille. Moreover, with a bottom CTD, it can detect environmental anomalies in classical hydrographic data, useful for oceanographers. As one of the rare station at the interface between the continental shelf and offshore, it will allow to observe the long-term evolution of the Northern Current in the context of climate change and anthropogenic pressure, and its potential varying impact on the Gulf of Lion. The data are of course also crucial for modellers. Moreover they show a great potential when supplementing other MOOSE data (glider and radar). Timeserie #1 - JULIO 1 - 12/02/2012 to 23/10/2012; JULIO (Judicious Location for Intrusions Observations) est situé à proximité de l'isobathe de 100 m de profondeur (environ 5,25°E et 43,13°N), au large de Marseille. Grâce à son ADCP (300 kHz), il permet de mesurer les courants horizontaux (tous les 4 m et toutes les ½ h) à travers la colonne d'eau et, entre autres, d'identifier les périodes d'échange entre le courant du Nord et le plateau continental. Il s'agit d'un élément crucial dans l'étude du gradient littoral-offshore de Marseille à la station MOOSE 42°N5°E, et des covariances potentielles avec le radar MIO et autres systèmes d'observation MIO ou internationaux, ainsi qu'avec le site SOMLIT (incluant également un ADCP) dans la baie de Marseille. De plus, avec un CTD de fond, il peut détecter les anomalies environnementales dans les données hydrographiques classiques, utiles aux océanographes. En tant qu'une des rares stations à l'interface entre le plateau continental et le large, elle permettra d'observer l'évolution à long terme du courant du Nord dans le contexte du changement climatique et de la pression anthropique, et son impact potentiel variable sur le Golfe du Lion. Les données sont bien sûr également cruciales pour les modélisateurs. De plus, ils présentent un grand potentiel en complément d'autres données MOOSE (planeur et radar). Série temporelle #1: - JULIO 1 - 12/02/2012 to 23/10/2012;
-

JULIO (Judicious Location for Intrusions Observations) mooring is located close to the 100 m-deep isobath (around 5.25°E and 43.13°N), offshore Marseille. With its bottom-moored (300kHz) ADCP, it enables measuring horizontal currents (every 4 m and every ½ h) through the water column, and among others, identifying periods of exchange between the Northern Current and the continental shelf. It is one crucial component in the study of the coastal-offshore gradient from Marseille to the MOOSE 42°N5°E station, and potential covariances with the MIO radar and other MIO or international observing systems, as well as with the SOMLIT site (including also an ADCP) in the bay of Marseille. Moreover, with a bottom CTD, it can detect environmental anomalies in classical hydrographic data, useful for oceanographers. As one of the rare station at the interface between the continental shelf and offshore, it will allow to observe the long-term evolution of the Northern Current in the context of climate change and anthropogenic pressure, and its potential varying impact on the Gulf of Lion. The data are of course also crucial for modellers. Moreover they show a great potential when supplementing other MOOSE data (glider and radar). Timeserie #2: - JULIO 2 - 17/09/2013 to 28/03/2014; JULIO (Judicious Location for Intrusions Observations) est situé à proximité de l'isobathe de 100 m de profondeur (environ 5,25°E et 43,13°N), au large de Marseille. Grâce à son ADCP (300 kHz), il permet de mesurer les courants horizontaux (tous les 4 m et toutes les ½ h) à travers la colonne d'eau et, entre autres, d'identifier les périodes d'échange entre le courant du Nord et le plateau continental. Il s'agit d'un élément crucial dans l'étude du gradient littoral-offshore de Marseille à la station MOOSE 42°N5°E, et des covariances potentielles avec le radar MIO et autres systèmes d'observation MIO ou internationaux, ainsi qu'avec le site SOMLIT (incluant également un ADCP) dans la baie de Marseille. De plus, avec un CTD de fond, il peut détecter les anomalies environnementales dans les données hydrographiques classiques, utiles aux océanographes. En tant qu'une des rares stations à l'interface entre le plateau continental et le large, elle permettra d'observer l'évolution à long terme du courant du Nord dans le contexte du changement climatique et de la pression anthropique, et son impact potentiel variable sur le Golfe du Lion. Les données sont bien sûr également cruciales pour les modélisateurs. De plus, ils présentent un grand potentiel en complément d'autres données MOOSE (planeur et radar). Série temporelle #2 : - JULIO 2 - 17/09/2013 to 28/03/2014;
-

JULIO (Judicious Location for Intrusions Observations) mooring is located close to the 100 m-deep isobath (around 5.25°E and 43.13°N), offshore Marseille. With its bottom-moored (300kHz) ADCP, it enables measuring horizontal currents (every 4 m and every ½ h) through the water column, and among others, identifying periods of exchange between the Northern Current and the continental shelf. It is one crucial component in the study of the coastal-offshore gradient from Marseille to the MOOSE 42°N5°E station, and potential covariances with the MIO radar and other MIO or international observing systems, as well as with the SOMLIT site (including also an ADCP) in the bay of Marseille. Moreover, with a bottom CTD, it can detect environmental anomalies in classical hydrographic data, useful for oceanographers. As one of the rare station at the interface between the continental shelf and offshore, it will allow to observe the long-term evolution of the Northern Current in the context of climate change and anthropogenic pressure, and its potential varying impact on the Gulf of Lion. The data are of course also crucial for modellers. Moreover they show a great potential when supplementing other MOOSE data (glider and radar). Timeserie #5 : - JULIO 5 - 01/09/2021 to 23/06/2022; JULIO (Judicious Location for Intrusions Observations) est situé à proximité de l'isobathe de 100 m de profondeur (environ 5,25°E et 43,13°N), au large de Marseille. Grâce à son ADCP (300 kHz), il permet de mesurer les courants horizontaux (tous les 4 m et toutes les ½ h) à travers la colonne d'eau et, entre autres, d'identifier les périodes d'échange entre le courant du Nord et le plateau continental. Il s'agit d'un élément crucial dans l'étude du gradient littoral-offshore de Marseille à la station MOOSE 42°N5°E, et des covariances potentielles avec le radar MIO et autres systèmes d'observation MIO ou internationaux, ainsi qu'avec le site SOMLIT (incluant également un ADCP) dans la baie de Marseille. De plus, avec un CTD de fond, il peut détecter les anomalies environnementales dans les données hydrographiques classiques, utiles aux océanographes. En tant qu'une des rares stations à l'interface entre le plateau continental et le large, elle permettra d'observer l'évolution à long terme du courant du Nord dans le contexte du changement climatique et de la pression anthropique, et son impact potentiel variable sur le Golfe du Lion. Les données sont bien sûr également cruciales pour les modélisateurs. De plus, ils présentent un grand potentiel en complément d'autres données MOOSE (planeur et radar). Série temporelle #5 : - JULIO 5 - 01/09/2021 to 23/06/2022;
-

JULIO (Judicious Location for Intrusions Observations) mooring is located close to the 100 m-deep isobath (around 5.25°E and 43.13°N), offshore Marseille. With its bottom-moored (300kHz) ADCP, it enables measuring horizontal currents (every 4 m and every ½ h) through the water column, and among others, identifying periods of exchange between the Northern Current and the continental shelf. It is one crucial component in the study of the coastal-offshore gradient from Marseille to the MOOSE 42°N5°E station, and potential covariances with the MIO radar and other MIO or international observing systems, as well as with the SOMLIT site (including also an ADCP) in the bay of Marseille. Moreover, with a bottom CTD, it can detect environmental anomalies in classical hydrographic data, useful for oceanographers. As one of the rare station at the interface between the continental shelf and offshore, it will allow to observe the long-term evolution of the Northern Current in the context of climate change and anthropogenic pressure, and its potential varying impact on the Gulf of Lion. The data are of course also crucial for modellers. Moreover they show a great potential when supplementing other MOOSE data (glider and radar). Timeserie #4 : - JULIO 4 - 07/12/2020 to 31/08/2021; JULIO (Judicious Location for Intrusions Observations) est situé à proximité de l'isobathe de 100 m de profondeur (environ 5,25°E et 43,13°N), au large de Marseille. Grâce à son ADCP (300 kHz), il permet de mesurer les courants horizontaux (tous les 4 m et toutes les ½ h) à travers la colonne d'eau et, entre autres, d'identifier les périodes d'échange entre le courant du Nord et le plateau continental. Il s'agit d'un élément crucial dans l'étude du gradient littoral-offshore de Marseille à la station MOOSE 42°N5°E, et des covariances potentielles avec le radar MIO et autres systèmes d'observation MIO ou internationaux, ainsi qu'avec le site SOMLIT (incluant également un ADCP) dans la baie de Marseille. De plus, avec un CTD de fond, il peut détecter les anomalies environnementales dans les données hydrographiques classiques, utiles aux océanographes. En tant qu'une des rares stations à l'interface entre le plateau continental et le large, elle permettra d'observer l'évolution à long terme du courant du Nord dans le contexte du changement climatique et de la pression anthropique, et son impact potentiel variable sur le Golfe du Lion. Les données sont bien sûr également cruciales pour les modélisateurs. De plus, ils présentent un grand potentiel en complément d'autres données MOOSE (planeur et radar). Série temporelle #4 : - JULIO 4 - 07/12/2020 to 31/08/2021;
-
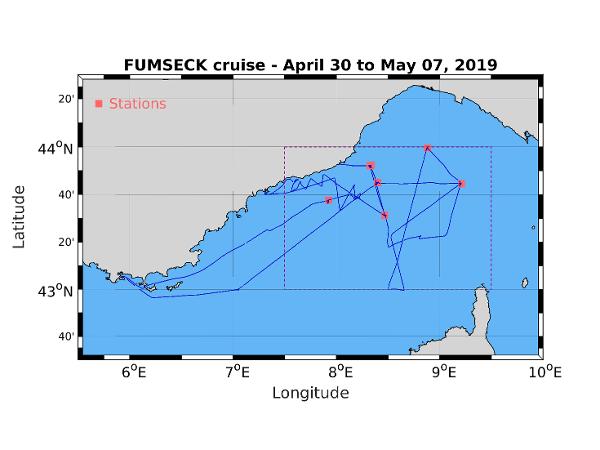
The FUMSECK (Facilities for Updating the Mediterranean Submesoscale - Ecosystem Coupling Knowledge) cruise aimed at performing technological tests of several instruments exploited for the study of the (sub)meso-scale processes and dynamics (from 0.1 to 100 km for a lifetime from several days to several weeks). Three categories of tests have been performed. The first category is the study of the MVP (Moving Vessel Profiler) tracked instruments behaviour, in particular the MSFFFII (Multi Sensor Free Fall Fish, so called "big fish"). We focused on the rotative behaviour of the big fish during its falling and raising, the connectics between the instrument and the MVP cable, between the platform and the boat depth sensor, and between the platform and the PC used to analyse the data, hence testing the whole data acquisition chain. The second category concerns the exploration of several methods to access the measurement of the current velocities vertical component, using different ADCP (Hull-mounted ADCP, Fixed-depth and profiling L-ADCP and Sentinel V (5 beams), Free-Fall ADCP), a prototype of a vertical velocity profiler, and a glider. Finally, we experimented the release of a sample of biodegradable coloured micro-particles at 15m-depth and within a 1 hectare surface, their tracking with drifting buoys, their extraction by pumping and their detection by cytometry. The goal of this experiment was its feasibility, in order to use these micro-particules as tracers for the understanding of the physical part of the ocean biological Carbon pump. Data acquired during the campain are : - Biological oceanography : * B08 Phytoplankton 7 days Continuous sampling for cytometer analysis. 15m-depth sampling for cytometer analysis (3 samples). 30.04.2019 * B90 Other biological/fisheries meas. 1 days GoPro images for the injection, the following and the sampling of coloured micro-particles. 30.04.2019 - Physical oceanography : * D05 Surface drifters/drifting buoys 3 deployments Injection, following, and sampling of coloured micro-particles at 15m-depth. Deployment and recovery of lagrangian drifters anchored at 15m for water mass following. 30.04.2019 * D71 Current profiler (eg ADCP) 7 days Continuous Vessel-Mounted ADCP. L-ADCP and Sentinel casts (5 and 6 stations). Free-Fall ADCP (6 stations). 30.04.2019 * D90 Other physical oceanographic meas. 7 days MVP (Moving Vessel Profiler) 30.04.2019 * D90 Other physical oceanographic meas. 6 stations VVP (Vertical Velocity Profiler) 30.04.2019 * H10 CTD stations 6 stations CTD casts 30.04.2019 * H71 Surface measurements underway (T,S) 7 days Continuous measurement 30.04.2019
 OSU Pytheas - Data Catalog
OSU Pytheas - Data Catalog