LPED UMR 151 AMU-IRD
Type of resources
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-

The Health and Demographic Surveillance System (HDSS) in Niakhar, a rural area of Senegal, is located 135 km east of Dakar. This HDSS has been set up in 1962 by the Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD) to face the shortcomings of the civil registration system and provide demographic indicators. Some 65 villages were followed annually in the Niakhar area from 1962 to 1969. The study zone was reduced to eight villages from 1969 to 1983, and from then on the HDSS was extended to include 22 other villages, covering a total of 30 villages for a population estimated at 45,000 in December 2013. Thus 8 villages have been under demographic surveillance for almost 50 years and 30 villages for 30years. Vital events, migrations, marital changes, pregnancies, immunization are routinely recorded (every four months). The database also includes epidemiological, economic and environmental information coming from specific surveys. Data were collected through annual rounds from 1962 to 1987; rounds became weekly from 1987 to 1997; routine visits were conducted every three months between 1997and 2007 and every four months since then. The current objectives are 1) to obtain a long-term assessment of demographic and socio-economic indicators necessary for bio-medical and social sciences research, 2) to keep up epidemiological and environmental monitoring, 3) to provide a research platform for clinical and interdisciplinary research (medical, social and environmental sciences). Research projects during the last 5 years are listed in Table 2. The Niakhar HDSS has institutional affiliation with the Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD, formerly ORSTOM). * Niakhar HDSS INDEPTH Core Dataset 1984-2016 (Release 2018). Provided by the INDEPTH Network Data Repository. http://indepth-ishare.org/index.php/catalog/132 * DOI : 10.7796/INDEPTH.SN013.CMD2016.v1 * https://doi.org/10.7796/INDEPTH.SN013.CMD2016.v1
-
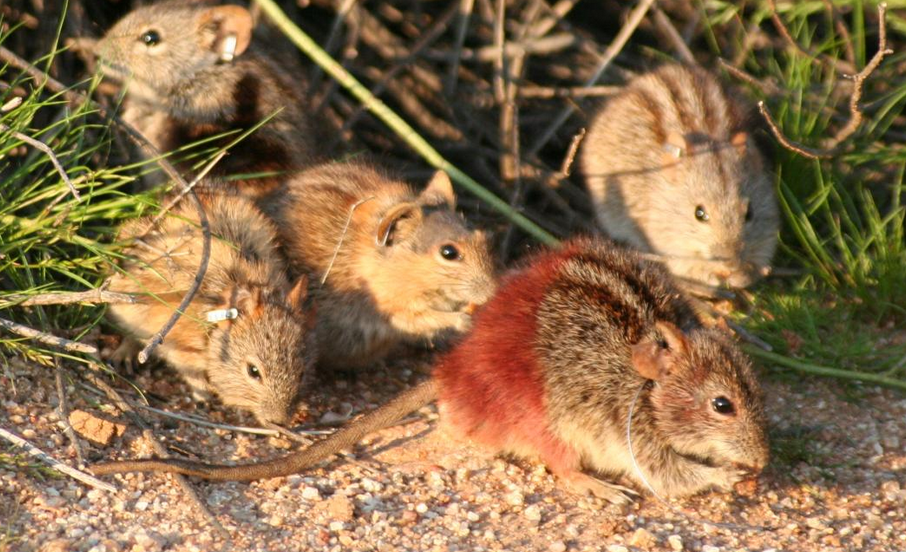

Suivi longitudinal sur 9 sites de terrain au Sénégal de l’observatoire ObsMiCE Paramètres mesurés: - détermination spécifique ; - indices d’abondance ; - données morphométriques, - estimation de l’âge, - paramètres de reproduction indicateurs de la dynamique des populations animales ; - prélèvements de tissus, d’ectoparasites et d’endoparasites ; - données environnementales ; - prévalence de parasites et pathogènes
-
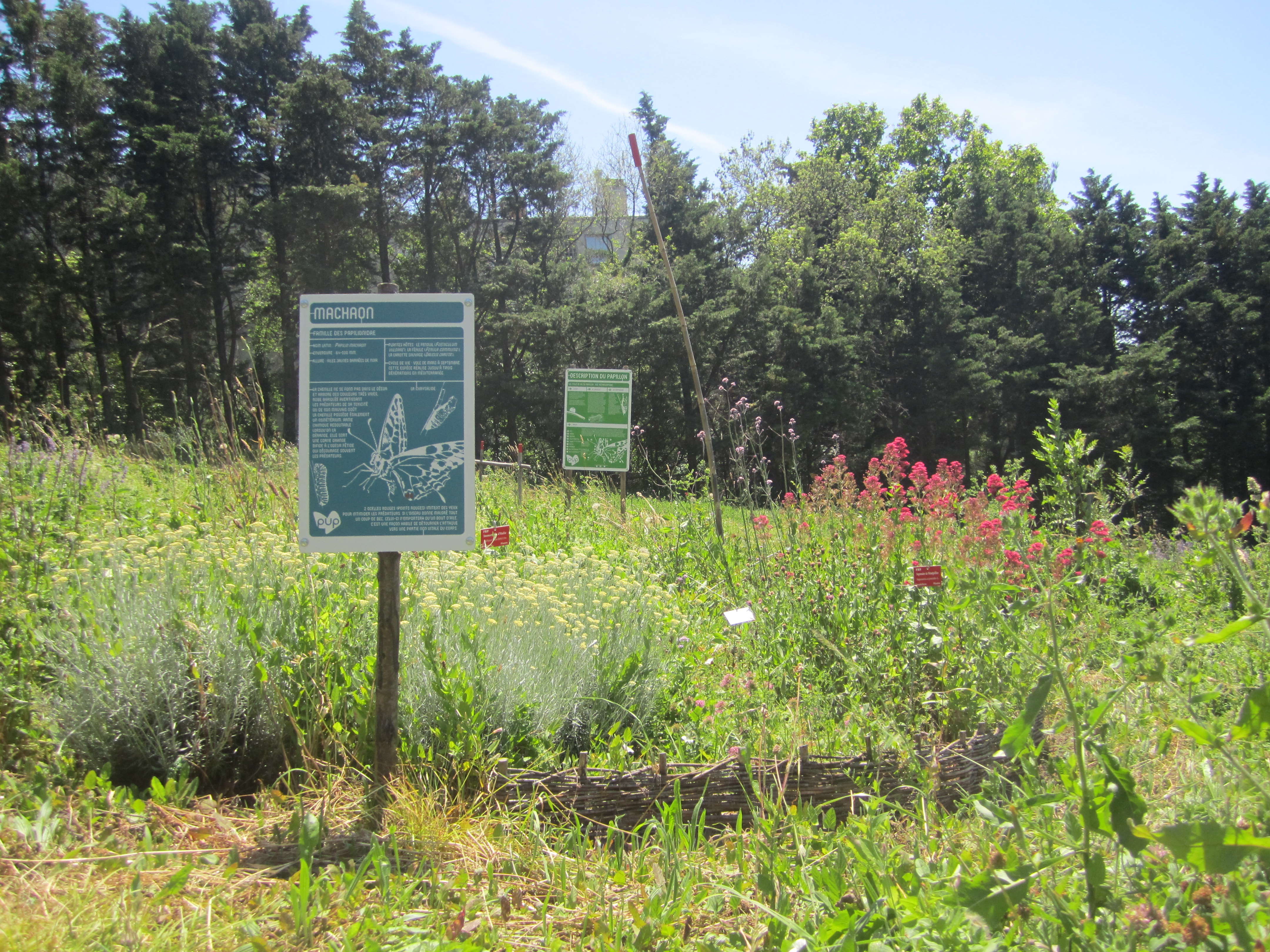

Communities of Rhopalocera (Lepidoptera) butterflies in 24 urban parks in Marseille Sampling of Rhopalocera communities: 7 to 12 transects in each of 24 urban parks in Marseille every 2 years since 2008. Increasing numbers of cities are currently developing sustainable policies aimed at promoting urban biodiversity and ecological dynamics through the planning of green networks and the implementation of more sustainable management practices. These human activities can strongly influence environmental factors on which the organization of ecological communities at different scales depends. Thus, it is of fundamental importance to understand the relative impact of local management, green space design and landscape features on the distribution and the abundance of species in urban areas. On the basis of 2 years of butterfly surveys in urban public parks within an extensive Mediterranean metropolitan area, Marseille (South-East France), the aim of this paper is to provide a better understanding of the effect of these three environmental scales (plot, park, landscape) on the composition and organization of species assemblages. Using variation partitioning and nestedness analysis on ecological data aggregated at plot-level and park-level respectively, we demonstrate the preponderant effect of landscape scale features on urban butterfly assemblages. Our results also highlight an important co-variation of plot management, park layout and urban landscape features, in their interaction with the community structure of urban butterflies. Although there is no significant species-area relationship, significantly nested patterns arise in species composition. Selective colonization appears as a driving force constraining the constitution of species assemblages within the city. However, a prospective study on adjacent more natural areas suggests that biotic limitations, interspecific competition and habitat filtering may play an important role if a larger portion of the urbanization gradient is explored, which remains to be investigated.
-

The Health and Demographic Surveillance System (HDSS) in Niakhar, a rural area of Senegal, is located 135 km east of Dakar. This HDSS has been set up in 1962 by the Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD) to face the shortcomings of the civil registration system and provide demographic indicators. Some 65 villages were followed annually in the Niakhar area from 1962 to 1969. The study zone was reduced to eight villages from 1969 to 1983, and from then on the HDSS was extended to include 22 other villages, covering a total of 30 villages for a population estimated at 45,000 in December 2013. Thus 8 villages have been under demographic surveillance for almost 50 years and 30 villages for 30years. Vital events, migrations, marital changes, pregnancies, immunization are routinely recorded (every four months). The database also includes epidemiological, economic and environmental information coming from specific surveys. Data were collected through annual rounds from 1962 to 1987; rounds became weekly from 1987 to 1997; routine visits were conducted every three months between 1997and 2007 and every four months since then. The current objectives are 1) to obtain a long-term assessment of demographic and socio-economic indicators necessary for bio-medical and social sciences research, 2) to keep up epidemiological and environmental monitoring, 3) to provide a research platform for clinical and interdisciplinary research (medical, social and environmental sciences). Research projects during the last 5 years are listed in Table 2. The Niakhar HDSS has institutional affiliation with the Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD, formerly ORSTOM). * Niakhar HDSS INDEPTH Core Dataset 1984-2016 (Release 2018). Provided by the INDEPTH Network Data Repository. www.indepth-network.og . * DOI : "10.7796/INDEPTH.SN011.CMD2016.v1" * https://doi.org/10.7796/INDEPTH.SN011.CMD2016.v1
-
In 1985 the population and health observatory was established at Mlomp, in the region of Ziguinchor, in southern Senegal (see map). The objective was to complement the two rural population observatories then existing in the country, Bandafassi, in the south-east, and Niakhar, in the centre-west, with a third observatory in a region - the south-west of the country (Casamance) - whose history, ethnic composition and economic situation were quite different from those of the regions where the first two observatories were located. It was expected that measuring the demographic levels and trends on those three sites would provide better coverage of the demographic and epidemiological diversity of the country. Following a population census in 1984-1985, demographic events and causes of death have been monitored yearly. During the initial census, all women were interviewed concerning the birth and survival of their children. Since 1985, yearly censuses, usually conducted in January-February, have been recording demographic data, including all births, deaths, and migrations. The completeness and accuracy of dates of birth and death are cross-checked against those of registers of the local maternity ward (_95% of all births) and dispensary (all deaths are recorded, including those occurring outside the area), respectively. The study area comprises 11 villages with approximately 8000 inhabitants, mostly Diola. Mlomp is located in the Department of Oussouye, Region of Ziguinchor (Casamance), 500 km south of Dakar. On 1 January 2000 the Mlomp area included a population of 7,591 residents living in 11 villages. The population density was 108 people per square kilometre. The population belongs to the Diola ethnic group, and the religion is predominantly animist, with a large minority of Christians and a few Muslims. Though low, the educational level - in 2000, 55% of women aged 15-49 had been to school (for at least one year) - is definitely higher than at Bandafassi. The population also benefits from much better health infrastructure and programmes. Since 1961, the area under study has been equipped with a private health centre run by French Catholic nurses and, since 1968, a village maternity centre where most women give birth. The vast majority of the children are totally immunized and involved in a growth-monitoring programme (Pison et al.,1993; Pison et al., 2001) * DOI : 10.7796/INDEPTH.SN012.CMD2016.v1 * DOI : https://doi.org/10.7796/INDEPTH.SN012.CMD2016.v1
 OSU Pytheas - Data Catalog
OSU Pytheas - Data Catalog