phytoplankton
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-

The New Caledonia lagoons show high seasonal and interannual variability (related to El Niño – Southern oscillation – ENSO - variability). They present a great diversity of local situations linked to differences in their geomorphology, to the nature of terrigenous inputs and to varied anthropogenic pressure. This variability impacts the structure of planktonic communities and their biodiversity. The scientific objectives of the CLAPPP project developed on 6 New Caledonia lagoons are : - 1) to describe the local environmental conditions and their seasonality, - 2) to understand the heterogeneity of phytoplankton communities at the biological, spatial and/or temporal levels, - 3) to study the role of this diversity in the functioning of coral ecosystems and the regulation of biogeochemical cycles, and - 4) to assess the importance of phytoplankton as an index of productivity and health of the lagoons in relation with local stress conditions and the risk of HABs. DOI: - https://doi.org/10.34930/2b52defe-e5f3-4fe2-9f2f-741d90e624ea Citation: Rodier, M., & Arfi, R. (2020). CLAPPP - New Caledonian lagoons: Physics and Phytoplankton processes [Data set]. MIO UMR 7294 CNRS. https://doi.org/10.34930/2B52DEFE-E5F3-4FE2-9F2F-741D90E624EA
-
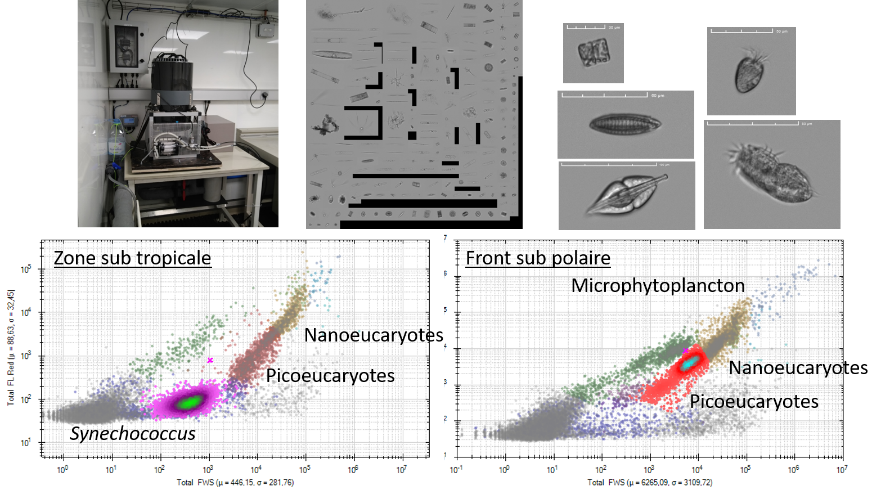
The MAP-IO (Marion Dusfresne Atmospheric Program - Indian Ocean) program aims to make up for the lack of observation in this region of the earth by equipping the Marion Dufresne vessel (https://taaf.fr/en/marion-dufresne-and-astrolabe/) with a set of in-situ instruments and remote sensing for the atmosphere and marine biology studies. This program has been labeled by the French Commission Nationale de la Flotte Hauturière (CNFH, https://www.flotteoceanographique.fr/) for the period 2021 to 2024. During this period, MAP-IO will operate as a scientific program for the acquisition and scientific enhancement of four years of data. This period will also serve as an operational prototype to study the feasibility of switching the program to a permanent observatory aimed at integration into international infrastructures networks such as ACTRIS (https://www.actris.eu/) or ICOS (https://www.icos-cp.eu/). - more informations on the project : http://www.mapio.re/ The Cytosense automated flow cytometer from the cytobuoy compagny was installed onboard the Marion Dufresnes Sea Water supply, to run semi continuously samples for phytoplankton functional groups resolution. Sample acquisition was schedulled once avery two hours. The data corresponds to abundances in cells/ml, mean forward scatter and red fluorescence in arbitrary units, per group. The groups are identified as standard groups following the BODC F02 vocabulary and the corresponding selections sets named following expert names.
-
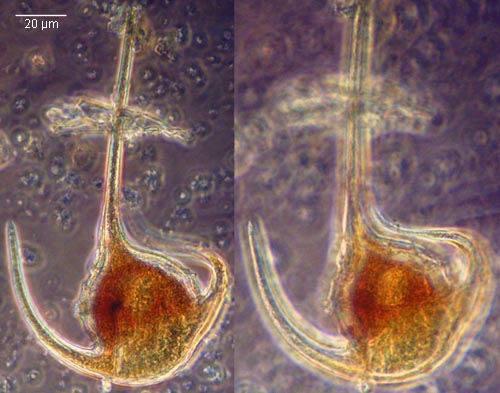
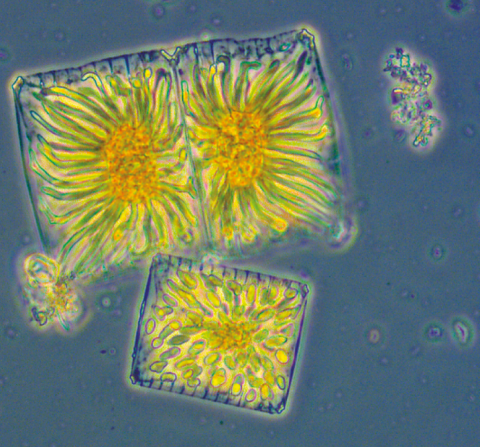
Données de l'analyse des peuplements phytoplanctoniques de la baie de Marseille. Dans le cadre du programme " Séries à long terme " du Service d'Observation du Centre d'Océanologie de Marseille, à partir de 1994, deux points de prélèvement. - Le premier (SOFCOM) correspond au point d'appui SOMLIT (Service d'Observation en Milieu Littoral de l'INSU), situé au large des îles du Frioul. Les prélèvements sont bimensuels, effectués en surface et dans la zone de fluorescence maximale, repérée au cours de la descente d'une bathysonde munie d'un capteur de fluorescence. Les données sont disponibles jusqu'en décembre 2004. - Le deuxième (CAPCOM) correspond aux prélèvements d'eau de surface réalisés dans l'Anse des Cuivres, au pied de la Station marine d'Endoume, entre mars 1994 et décembre 2000. Ces échantillons sont pris comme référence de la frange littorale extrême. La fréquence de prélèvements de cette série a varié de 1/3 jours à 1/8. Pour les deux séries des paramètres physico-chimiques et hydrologiques sont disponibles sur le site du Service d'Observation Informations Taxonomiques Une fiche avec des Renseignements taxonomiques est disponible pour les espèces observées en Méditerranée au cours des analyses. Elle comprend : - le nom complet, l'autorité, les synonymes connus, - dans certains cas, un dessin ou une photo. - le volume moyen calculé à partir de mesures réalisées sur les données récentes. - les caractéristiques écologiques. Des liens permettent de retrouver la liste des prélèvements dans lequels une espèce a été observée, ainsi que la bibliographie qui la concerne
-
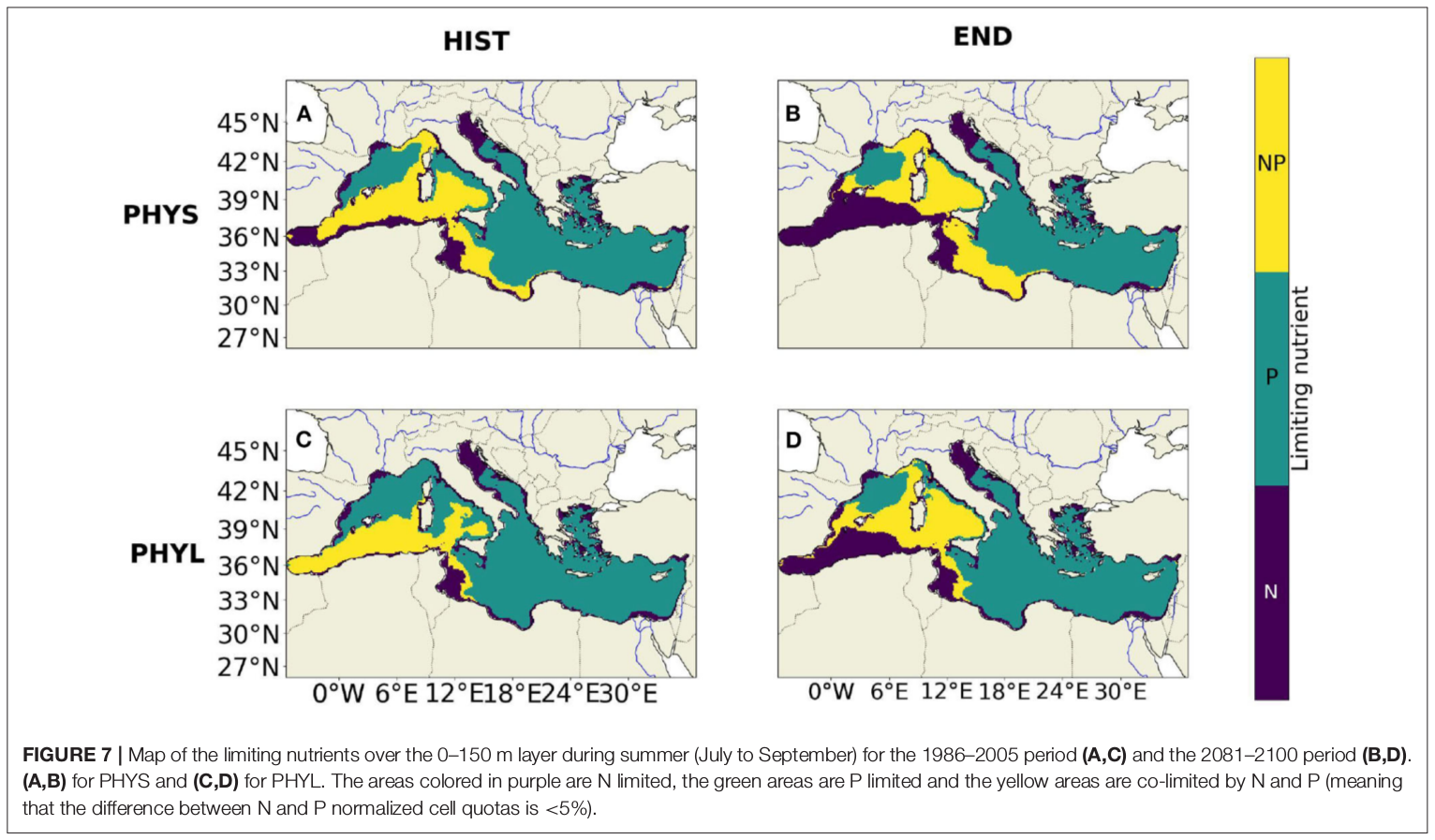
"Towards an integrated prediction of Land & Sea Responses to global change in the Mediterranean Basin" The LaSeR-Med project aims at investigating the effects of climate change and of mediterranean population growth on some major indicators of the Mediterranean Sea (primary production, carbon export, zooplankton biomass available for small pelagic fishes, pH, dissolved oxygen) using and integrated model encompassing a socio-economic model, a continental model of agro-ecosystems, and a physical ocean-atmosphere model coupled to a biogeochemical model of the ocean. Last, a model for the widespread species of jellyfish Pelagia Noctiluca (Berline et al., 2013) uses biogeochemical outputs as food forcing for the jellyfish. In this project, our aim was first to investigate the large-scale and long-term impacts of variations in river inputs on the biogeochemistry of the Mediterranean Sea over the last decades (see Pages et al., 2020a). In the second phase, a climate scenario (RCP8.5) alone (Pages et al., 2020b) or combined with a “land-use” scenario derived to ensure the same level of food availability as today in 2050 have been run to investigate its effect on these indicators and to analyze the observed changes on the structure and the functioning of planktonic food web. This interdisciplinary project provided the framework for joint discussions on each of the sub-models that constitute the integrated model, namely the socio-economic model (Ami et al., in prep., Mardesic et al., in prep.) created ex nihilo by researchers from AMSE, INRA and GREQAM, the continental agro-ecosystem model LPJmL (Bondeau et al., 2007) worked on at IMBE so as to include the nitrogen and phosphorous cycles in the frame of the present project, and the ocean biogeochemical model Eco3M-Med developed at MIO (Baklouti et al., 2006; Alekseenko et al. 2014, Guyennon et al., 2015; Pagès et al., 2020a), forced by ocean physics, either using the ocean model NEMO-Med12 forced by atmosphere at IPSL (simulation NM12-FREE run with the NEMO-MED12 model and used for our hindcast simulation, see below) or a coupled ocean-atmosphere model at CNRM (physical forcing provided by CNRM-RCSM4, see below). Details on the CNRM-RCSM4 model The CNRM-RCSM4 simulates the main components of the Mediterranean regional climate system and their interactions. It includes four different components: (i) The atmospheric regional model ALADIN-Climate (Radu et al., 2008; Colin et al., 2010; Herrmann et al., 2011) characterized by a 50 km horizontal resolution, 31 vertical levels, and a time step of 1800 s, (ii) the ISBA (Interaction between Soil Biosphere and Atmosphere) land-surface model (Noilhan and Mahfouf, 1996) at a 50 km horizontal resolution, (iii) the TRIP (Total Runoff Integrating Pathways) river routing model (Oki and Sud, 1998), used to convert the runoff simulated by ISBA into rivers (Decharme et al., 2010; Szczypta et al., 2012; Voldoire et al., 2013), and (iv) the Ocean general circulation model NEMO (Nucleus for European Modeling of the Ocean, Madec and NEMO-Team, 2016) in its NEMO-MED8 regional configuration (Beuvier et al., 2010). NEMO-MED8 is characterized by a horizontal resolution of 1/8° (grid cells size from 6 to 12 km), a vertical resolution of 43 vertical levels (cell height ranging from 6 to 200 m), and a time step of 1200 s. More details about the CNRM-RCSM4 model can be found in Sevault et al. (2014). Keywords: - Mediterranean Sea, river inputs, chlorophyll, nutrients, phytoplankton, bacteria, zooplankton, dissolved and particulate organic detrital matter Citation: Pagès, R., Baklouti, M., Barrier, N., Richon, C., Dutay, J.-C., and Moutin, T. (2020a). Changes in rivers inputs during the last decades significantly impacted the biogeochemistry of the eastern Mediterranean basin: a modelling study. Prog. Oceanogr. 181:102242. doi:10.1016/j.pocean.2019.102242 Pagès, R., Baklouti, M., Barrier, N., Ayache, M., Sevault, F., Somot, S. and Moutin, T. (2020b). Projected Effects of Climate-Induced Changes in Hydrodynamics on the Biogeochemistry of the Mediterranean Sea Under the RCP 8.5 Regional Climate Scenario. Front. Mar. Sci. 7:563615. doi:10.3389/fmars.2020.563615 Ayache, M., Bondeau, A., Pagès, R., Barrier, N., Ostberg, S. and Baklouti, M. (2020). LPJmL-Med – Modelling the dynamics of the land-sea nutrient transfer over the Mediterranean region–version 1: Model description and evaluation. Geoscientific Model Development Discussions, Copernicus Publ.
-
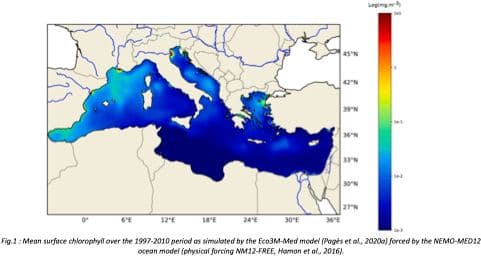
"Towards an integrated prediction of Land & Sea Responses to global change in the Mediterranean Basin" The LaSeR-Med project aims at investigating the effects of climate change and of mediterranean population growth on some major indicators of the Mediterranean Sea (primary production, carbon export, zooplankton biomass available for small pelagic fishes, pH, dissolved oxygen) using and integrated model encompassing a socio-economic model, a continental model of agro-ecosystems, and a physical ocean-atmosphere model coupled to a biogeochemical model of the ocean. Last, a model for the widespread species of jellyfish Pelagia Noctiluca (Berline et al., 2013) uses biogeochemical outputs as food forcing for the jellyfish. In this project, our first aim was to investigate the large-scale and long-term impacts of variations in river inputs on the biogeochemistry of the Mediterranean Sea over the last decades (see Pages et al., 2020a). This interdisciplinary project provided the framework for joint discussions on each of the sub-models that constitute the integrated model, namely the socio-economic model (Ami et al., in prep., Mardesic et al., in prep.) created ex nihilo by researchers from AMSE, INRA and GREQAM, the continental agro-ecosystem model LPJmL (Bondeau et al., 2007) worked on at IMBE so as to include the nitrogen and phosphorous cycles in the frame of the present project, and the ocean biogeochemical model Eco3M-Med developed at MIO (Baklouti et al., 2006; Alekseenko et al. 2014, Guyennon et al., 2015; Pagès et al., 2020a), forced by ocean physics, either using the ocean model NEMO-Med12 forced by atmosphere at IPSL (simulation NM12-FREE run with the NEMO-MED12 model and used for our hindcast simulation, see below) or a coupled ocean-atmosphere model at CNRM (physical forcing provided by CNRM-RCSM4, see below). Details on simulation NM12-free: The historical simulation used in this work is referred to as the NM12-FREE (no reanalysis no data assimilation) which started in October 1979 and ended in June 2013 (Hamon et al., 2016). It has been run with the general circulation model NEMO in its regional configuration NEMO-MED12 based on a horizontal resolution of 1/12 de degree (6.5 to 8 km cells) and a 75-level vertical resolution (of 1 m width at the surface to 135 m at the seabed). For this simulation, runoff and river inputs in the NM12 domain came from the inter-annual data of Ludwig et al. (2009) and the atmospheric forcing was based on the dynamical downscaling of the ERA-INTERIM reanalysis, i.e. ALDERA which has a 12 km spatial resolution and a 3 h temporal resolution. More details on the NM12-FREE simulation are given in Hamon et al. (2016). Keywords: - Mediterranean Sea, river inputs, chlorophyll, nutrients, phytoplankton, bacteria, zooplankton, dissolved and particulate organic detrital matter Citation: Pagès, R., Baklouti, M., Barrier, N., Richon, C., Dutay, J.-C., and Moutin, T. (2020a). Changes in rivers inputs during the last decades significantly impacted the biogeochemistry of the eastern Mediterranean basin: a modelling study. Prog. Oceanogr. 181:102242. doi:10.1016/j.pocean.2019.102242 Ayache, M., Bondeau, A., Pagès, R., Barrier, N., Ostberg, S. and Baklouti, M. (2020). LPJmL-Med – Modelling the dynamics of the land-sea nutrient transfer over the Mediterranean region–version 1: Model description and evaluation. Geoscientific Model Development Discussions, Copernicus Publ.
 OSU Pytheas - Data Catalog
OSU Pytheas - Data Catalog