modelling
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
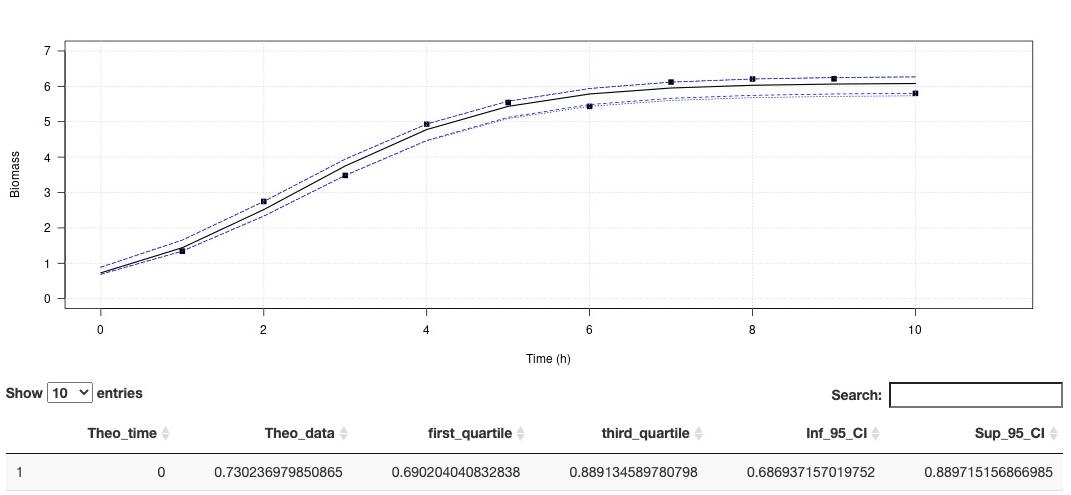
Environmental conditions are a set of physical and biological variables that define an ecosystem. Microorganisms with higher generation times than more complex multicellular organisms are more sensitive to changing environmental conditions. Therefore, microbial growth curves are an important and simple way to understand how environmental conditions affect microorganisms. Growth curves are used in a variety of biological applications. Traditionally in microbiology, the maximum growth rate (µmax) is calculated by fitting a linear model on data of the exponential growth phase. This method is simple to implement, and robust if the exponential phase contains many points. However, this method is very limiting when the curve is described with few points, as we have seen with experiments under high pressure conditions. In order to overcome this limit, recurrent in biology, we propose to use models to estimate growths parameters. Modeling has existed for many years to describe the growth behavior of microorganisms under variable physical and chemical conditions (Zwietering et al., 1990). Here we propose a ready-to-use application that do not require any special coding skills and allow retrieving several essential parameters describing microbial growth. his app aims at estimating the growth rate and maximum cells density using non-linear regression. The method is detailled in Martini et al. (2013). A demo dataset is available in "Download a demo dataset", you can save it in your computer and load it using "Browse", or you can also browse your own dataset. On Plot panel, it is possible to set axes labels, axes range and Smooth. Smooth parameter can compute theorical (downloadable) for to use with other activities. In order to run this application, you have to format your dataset with tabulation separators. Also, remove all spaces in the dataset header (prefer to use "_" when needed). Organise your dataset so that there is only two arrays. The first one being the time and the second one, the cells density (e. g. optic density, cell number, biomass). This application proposes a method to perform a logistic regression to estimate growth rate as well as maximum cells density . Citation: Garel, M., Izard, L., Vienne, M., Nerini, D., Tamburini, C., Martini, S. (2021). R-shiny-microorganisms v2 : A ready-to-use logistic regression implemented in R shiny to estimate growth parameters of microorganisms [Data set]. MIO UMR 7294 CNRS. https://doi.org/10.34930/DC1DAF1C-09E3-4829-8878-91D0BF0E643E
-
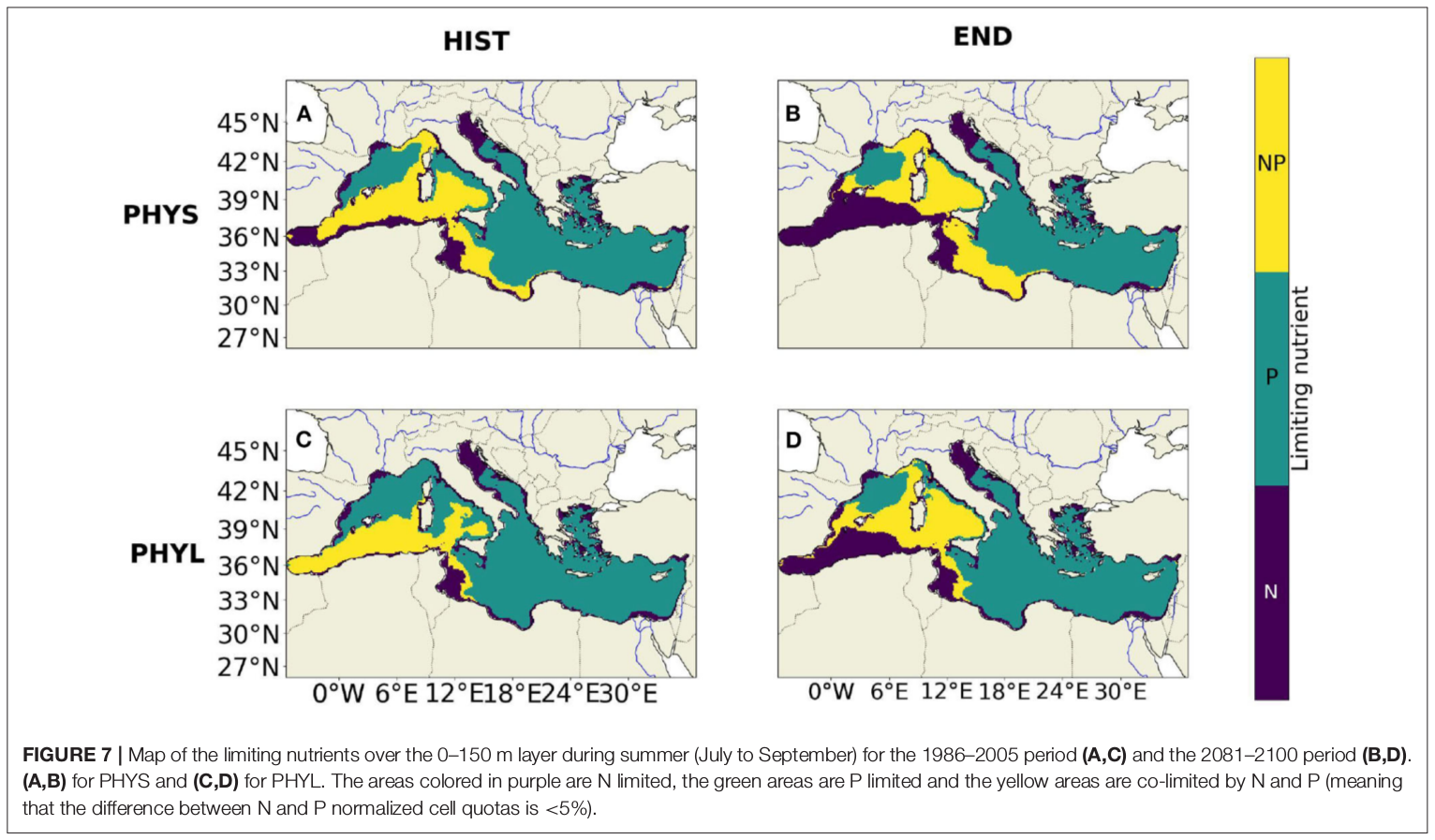
"Towards an integrated prediction of Land & Sea Responses to global change in the Mediterranean Basin" The LaSeR-Med project aims at investigating the effects of climate change and of mediterranean population growth on some major indicators of the Mediterranean Sea (primary production, carbon export, zooplankton biomass available for small pelagic fishes, pH, dissolved oxygen) using and integrated model encompassing a socio-economic model, a continental model of agro-ecosystems, and a physical ocean-atmosphere model coupled to a biogeochemical model of the ocean. Last, a model for the widespread species of jellyfish Pelagia Noctiluca (Berline et al., 2013) uses biogeochemical outputs as food forcing for the jellyfish. In this project, our aim was first to investigate the large-scale and long-term impacts of variations in river inputs on the biogeochemistry of the Mediterranean Sea over the last decades (see Pages et al., 2020a). In the second phase, a climate scenario (RCP8.5) alone (Pages et al., 2020b) or combined with a “land-use” scenario derived to ensure the same level of food availability as today in 2050 have been run to investigate its effect on these indicators and to analyze the observed changes on the structure and the functioning of planktonic food web. This interdisciplinary project provided the framework for joint discussions on each of the sub-models that constitute the integrated model, namely the socio-economic model (Ami et al., in prep., Mardesic et al., in prep.) created ex nihilo by researchers from AMSE, INRA and GREQAM, the continental agro-ecosystem model LPJmL (Bondeau et al., 2007) worked on at IMBE so as to include the nitrogen and phosphorous cycles in the frame of the present project, and the ocean biogeochemical model Eco3M-Med developed at MIO (Baklouti et al., 2006; Alekseenko et al. 2014, Guyennon et al., 2015; Pagès et al., 2020a), forced by ocean physics, either using the ocean model NEMO-Med12 forced by atmosphere at IPSL (simulation NM12-FREE run with the NEMO-MED12 model and used for our hindcast simulation, see below) or a coupled ocean-atmosphere model at CNRM (physical forcing provided by CNRM-RCSM4, see below). Details on the CNRM-RCSM4 model The CNRM-RCSM4 simulates the main components of the Mediterranean regional climate system and their interactions. It includes four different components: (i) The atmospheric regional model ALADIN-Climate (Radu et al., 2008; Colin et al., 2010; Herrmann et al., 2011) characterized by a 50 km horizontal resolution, 31 vertical levels, and a time step of 1800 s, (ii) the ISBA (Interaction between Soil Biosphere and Atmosphere) land-surface model (Noilhan and Mahfouf, 1996) at a 50 km horizontal resolution, (iii) the TRIP (Total Runoff Integrating Pathways) river routing model (Oki and Sud, 1998), used to convert the runoff simulated by ISBA into rivers (Decharme et al., 2010; Szczypta et al., 2012; Voldoire et al., 2013), and (iv) the Ocean general circulation model NEMO (Nucleus for European Modeling of the Ocean, Madec and NEMO-Team, 2016) in its NEMO-MED8 regional configuration (Beuvier et al., 2010). NEMO-MED8 is characterized by a horizontal resolution of 1/8° (grid cells size from 6 to 12 km), a vertical resolution of 43 vertical levels (cell height ranging from 6 to 200 m), and a time step of 1200 s. More details about the CNRM-RCSM4 model can be found in Sevault et al. (2014). Keywords: - Mediterranean Sea, river inputs, chlorophyll, nutrients, phytoplankton, bacteria, zooplankton, dissolved and particulate organic detrital matter Citation: Pagès, R., Baklouti, M., Barrier, N., Richon, C., Dutay, J.-C., and Moutin, T. (2020a). Changes in rivers inputs during the last decades significantly impacted the biogeochemistry of the eastern Mediterranean basin: a modelling study. Prog. Oceanogr. 181:102242. doi:10.1016/j.pocean.2019.102242 Pagès, R., Baklouti, M., Barrier, N., Ayache, M., Sevault, F., Somot, S. and Moutin, T. (2020b). Projected Effects of Climate-Induced Changes in Hydrodynamics on the Biogeochemistry of the Mediterranean Sea Under the RCP 8.5 Regional Climate Scenario. Front. Mar. Sci. 7:563615. doi:10.3389/fmars.2020.563615 Ayache, M., Bondeau, A., Pagès, R., Barrier, N., Ostberg, S. and Baklouti, M. (2020). LPJmL-Med – Modelling the dynamics of the land-sea nutrient transfer over the Mediterranean region–version 1: Model description and evaluation. Geoscientific Model Development Discussions, Copernicus Publ.
-
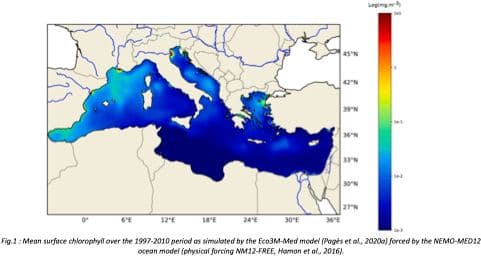
"Towards an integrated prediction of Land & Sea Responses to global change in the Mediterranean Basin" The LaSeR-Med project aims at investigating the effects of climate change and of mediterranean population growth on some major indicators of the Mediterranean Sea (primary production, carbon export, zooplankton biomass available for small pelagic fishes, pH, dissolved oxygen) using and integrated model encompassing a socio-economic model, a continental model of agro-ecosystems, and a physical ocean-atmosphere model coupled to a biogeochemical model of the ocean. Last, a model for the widespread species of jellyfish Pelagia Noctiluca (Berline et al., 2013) uses biogeochemical outputs as food forcing for the jellyfish. In this project, our first aim was to investigate the large-scale and long-term impacts of variations in river inputs on the biogeochemistry of the Mediterranean Sea over the last decades (see Pages et al., 2020a). This interdisciplinary project provided the framework for joint discussions on each of the sub-models that constitute the integrated model, namely the socio-economic model (Ami et al., in prep., Mardesic et al., in prep.) created ex nihilo by researchers from AMSE, INRA and GREQAM, the continental agro-ecosystem model LPJmL (Bondeau et al., 2007) worked on at IMBE so as to include the nitrogen and phosphorous cycles in the frame of the present project, and the ocean biogeochemical model Eco3M-Med developed at MIO (Baklouti et al., 2006; Alekseenko et al. 2014, Guyennon et al., 2015; Pagès et al., 2020a), forced by ocean physics, either using the ocean model NEMO-Med12 forced by atmosphere at IPSL (simulation NM12-FREE run with the NEMO-MED12 model and used for our hindcast simulation, see below) or a coupled ocean-atmosphere model at CNRM (physical forcing provided by CNRM-RCSM4, see below). Details on simulation NM12-free: The historical simulation used in this work is referred to as the NM12-FREE (no reanalysis no data assimilation) which started in October 1979 and ended in June 2013 (Hamon et al., 2016). It has been run with the general circulation model NEMO in its regional configuration NEMO-MED12 based on a horizontal resolution of 1/12 de degree (6.5 to 8 km cells) and a 75-level vertical resolution (of 1 m width at the surface to 135 m at the seabed). For this simulation, runoff and river inputs in the NM12 domain came from the inter-annual data of Ludwig et al. (2009) and the atmospheric forcing was based on the dynamical downscaling of the ERA-INTERIM reanalysis, i.e. ALDERA which has a 12 km spatial resolution and a 3 h temporal resolution. More details on the NM12-FREE simulation are given in Hamon et al. (2016). Keywords: - Mediterranean Sea, river inputs, chlorophyll, nutrients, phytoplankton, bacteria, zooplankton, dissolved and particulate organic detrital matter Citation: Pagès, R., Baklouti, M., Barrier, N., Richon, C., Dutay, J.-C., and Moutin, T. (2020a). Changes in rivers inputs during the last decades significantly impacted the biogeochemistry of the eastern Mediterranean basin: a modelling study. Prog. Oceanogr. 181:102242. doi:10.1016/j.pocean.2019.102242 Ayache, M., Bondeau, A., Pagès, R., Barrier, N., Ostberg, S. and Baklouti, M. (2020). LPJmL-Med – Modelling the dynamics of the land-sea nutrient transfer over the Mediterranean region–version 1: Model description and evaluation. Geoscientific Model Development Discussions, Copernicus Publ.
 OSU Pytheas - Data Catalog
OSU Pytheas - Data Catalog